- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- Wireless ConnectivityWireless Connectivity
- RFID / NFCRFID / NFC
- Advanced AnalogAdvanced Analog
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
- S32Z/E
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- Generative AI & LLMs
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
- RFID / NFC
- Advanced Analog
-
- NXP Tech Blogs
- Home
- :
- i.MX Processors
- :
- i.MX Processors Knowledge Base
- :
- i.MX Power Profiling: Triple-range Smart Current Sensor
i.MX Power Profiling: Triple-range Smart Current Sensor
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
i.MX Power Profiling: Triple-range Smart Current Sensor
i.MX Power Profiling: Triple-range Smart Current Sensor
NOTE: Always de-power the target board and the aggregator when plugging or unplugging smart sensors from the aggregator.
NOTE: See this link to instrument a board with a Smart Sensor.
This page documents the triple-range "smart" current sensor that's part of a larger system for profiling power on application boards. The smart sensor features a Kinetis KL05Z with three current sense amplifiers. It allows measurement currents in three ranges. Four assembly options allow measurement of rail voltages 0-3.3V (two overall current ranges), 0-6.6V, and 12V. It connects to an aggregator, which powers, controls and aggregates data from a number of smart sensor boards.
One of the biggest improvements over the older dual-range measurement system is that the on-sensor microcontroller allows near-simultaneous measurement of all instrumented rails on a board. The dual range profiler can only make one measurement at a time.
These are intended to be used with a microncontroller board to act as a trigger and data aggregator. This aggregator could also be used to reprogram the sensors.
The series resistance added by the smart sensor when in run mode (highest current range) is under 11 milliOhms as measured with 4-point probes and a Keysight B2902B SMU.
A "power oscilloscope" can be made by triggering measurements at regular intervals and presenting the results graphically....
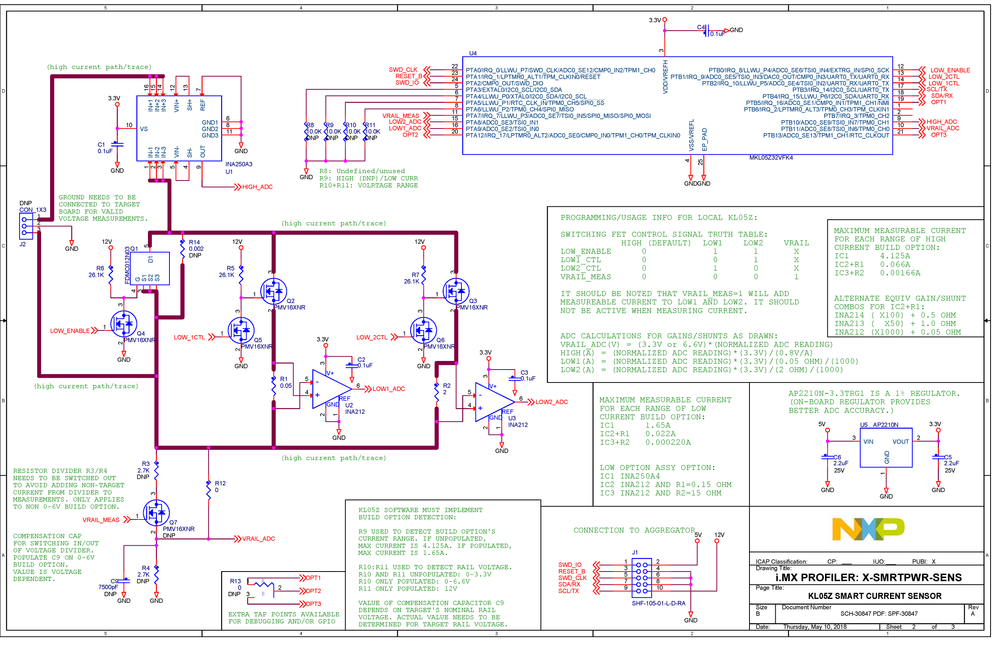
Schematic:
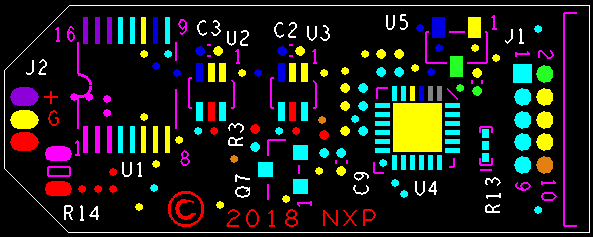
Board Layout, Top:
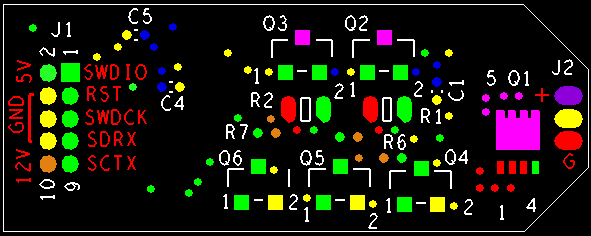
Board Layout, Bottom:
Here's a photo of two with a nickel is included to show scale. The board measures about 0.5 by 1.3 inches.
Connections:
The smart sensor header connections are:
- 5V: powers the 3.3V regulator, which in turn powers everything else on the sensor board
- 12V: all the gates of all the switching FETs are pulled pulled up to 12V
- GND: ground connection
- SCL/TX: I2C clock line
- SDA/RX: I2C data line
- SWD_CLK: line for triggering smart sensors to make measurements
- RESET_B: line for resetting the smart sensor board
- SWD_IO: select line for the smart sensor
Theory of operation:
Three shunts and current sense amplifiers are used to measure current in three ranges. One shunt/sense amp pair has a 0.002Ω shunt integrated into the IC package (U1, INA250). The other two sense amps (U2 and U3, INA212) require an external shunt.
FETs Q1, Q2, and Q3 are used to switch the two lower range shunt/sense amp pairs in and out of circuit. In normal run operation (highest current range), Q1 (FDMC012N03, with Rds(on) under 1.5mΩ) is turned on, which shorts leaves only U1 in circuit. FETs Q4, Q5 and Q6 translate the voltages to 3.3V so that GPIO on U4 (MCU KL05Z) can control them.
Rail voltage measurement is facilitated via resistors R3, R4, and R12 and Q7. Not all of these are populated in every assembly option. For measuring rail voltages 0-3.3V, R12 is populated. To measure 0-6.6V, R3, R4,and Q7 are populated. When turned on Q7 enables the voltage divider. All of the assembly option population info can be found in the schematic (attached).
Regulator U5 (AP2210N) provides the 3.3V supply for all of the components on the board. This 1% tolerance regulator is used to provide a good reference for the ADC in U4.
Microcontroller U4 detects the assembly population option of the board via resistors R9, R10, and R11 so that the same application code can be used across all variations of the sensor boards. GPIO control the FETs and four ADC channels are used to measure the sense amplifier outputs and the rail voltage. Having a microcontroller on the sensor board allows the user to do extra credit things like count coulombs as well as allowing all similarly instrumented rails to measure at the same time via trigger line SWD_CLK. Data communication can be via I2C or UART, since these two pins can do both. But if multiple sensor boards are to be used with an aggregator, communication needs to be over I2C.
Application Code:
The latest application code for the KL05Z on the smart sensor resides here: https://os.mbed.com/users/r14793/code/30847-SMRTSNSR-KL05Z/. The latest binary is attached below.
In order to re-flash a smart sensor, the modification detailed in the aggregator page needs to be made. Once the modification is completed, leave the aggregator unpowered while pluging the SWD debugger into J5 and the smart sensor to be programmed into JP15.
Very old UART-based application code for the KL05Z, built in the on-line MBED compiler (note that it requires the modified mbed library for internal oscillator). This code was used while testing the first smart sensor prototypes. It has since been abandoned. It's published here in the event that a user wants to use a single sensor plugged into JP15 with UART breakout connector J6.
/******************************************************************************
*
* MIT License (https://spdx.org/licenses/MIT.html)
* Copyright 2017-2018 NXP
*
* MBED code for KL05Z-based "smart" current sensor board, basic testing
* of functions via UART (connected via FRDM board and OpenSDA USB virtual
* COM port).
*
* Eventual goal is to have each smart sensor communicate over I2C to an
* aggregator board (FRDM board with a custom shield), allowing 1-10 power
* supply rails to be instrumented. Extra credit effort is to support
* sensors and aggregator with sigrok...
*
* Because there is no crystal on the board, need to edit source mbed-dev library
* to use internal oscillator with pound-define:
* change to "#define CLOCK_SETUP 0" in file:
* mbed-dev/targets/TARGET_Freescale/TARGET_KLXX/TARGET_KL05Z/device/system_MKL05Z4.c
*
******************************************************************************/
#include "mbed.h"
// These will be GPIO for programming I2C address...
// not yet implemented, using as test pins...
DigitalOut addr0(PTA3);
DigitalOut addr1(PTA4);
DigitalOut addr2(PTA5);
DigitalOut addr3(PTA6);
// configure pins for measurements...
// analog inputs from sense amps and rail voltage divider...
AnalogIn HIGH_ADC(PTB10);
AnalogIn VRAIL_ADC(PTB11);
AnalogIn LOW1_ADC(PTA9);
AnalogIn LOW2_ADC(PTA8);
// outputs which control switching FETs...
DigitalOut VRAIL_MEAS(PTA7); // turns on Q7, connecting voltage divider
DigitalOut LOW_ENABLE(PTB0); // turns on Q4, turning off Q1, enabling low measurement
DigitalOut LOW1(PTB2); // turns on Q5, turning off Q2, disconnecting shunt R1
DigitalOut LOW2(PTB1); // turns on Q6, turning off Q3, disconnecting shunt R2
// input used for triggering measurement...
// will eventually need to be set up as an interrupt so it minimizes delay before measurement
InterruptIn trigger(PTA0); // use as a trigger to make measurement...
// PTB3/4 can be used as UART or I2C...
// For easier development with one smart sensor, we are using UART here...
Serial uart(PTB3, PTB4); // tx, rx
long int count=0;
int n=25; // global number of averages for each measurement
int i, temp;
bool repeat=true; // flag indicating whether measurements should repeat or not
const float vref = 3.3; // set vref for use in calculations...
float delay=0.25; // default delay between measurement
bool gui = false; // flag for controlling human vs machine readable output
bool statistics = false;// flag for outputting min and max along with average (GUI mode only)
void enableHighRange(){
LOW_ENABLE = 0; // short both low current shunts, close Q1
wait_us(5); // delay for FET to settle... (make before break)
LOW1 = 0; LOW2 = 0; // connect both shunts to make lower series resistance
VRAIL_MEAS = 0; // disconnect rail voltage divider
wait_us(250); // wait for B2902A settling...
}
void enableLow1Range(){
LOW1 = 0; LOW2 = 1; // disconnect LOW2 shunt so LOW1 can measure
wait_us(5); // delay for FET to settle... (make before break)
LOW_ENABLE = 1; // unshort low current shunts, open Q1
VRAIL_MEAS = 0; // disconnect rail voltage divider
wait_us(250); // wait for B2902A settling...
}
void enableLow2Range(){
LOW1 = 1; LOW2 = 0; // disconnect LOW1 shunt so LOW2 can measure
wait_us(5); // delay for FET to settle... (make before break)
LOW_ENABLE = 1; // unshort low current shunts, open Q1
VRAIL_MEAS = 0; // disconnect rail voltage divider
wait_us(500); // wait for B2902A settling...
}
void enableRailV(){
VRAIL_MEAS = 1; // turn on Q7, to enable R3-R4 voltage divider
wait_us(125); // wait for divider to settle...
// Compensation cap can be used to make
// voltage at ADC a "square wave" but it is
// rail voltage and FET dependent. Cap will
// need tuning if this wait time is to be
// removed/reduced.
//
// So, as it turns out, this settling time and
// compensation capacitance are voltage dependent
// because of the depletion region changes in the
// FET. Reminiscent of grad school and DLTS.
// Gotta love device physics...
}
void disableRailV(){
VRAIL_MEAS = 0; // turn off Q7, disabling R3-R4 voltage divider
}
// this function measures current, autoranging as necessary
// to get the best measurement...
void measureAuto(){
Timer t;
float itemp;
float tempI=0;
float imin = 1.0; // used to keep track of the minimum...
float imax = 0; // used to keep track of the maximum...
t.start(); // use timer to see how long things take...
enableHighRange(); // this should already be the case, but do it anyway...
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
itemp = HIGH_ADC; // read HIGH range sense amp output
if (statistics && itemp>imax) imax = itemp; // update max if necessary
if (statistics && itemp<imin) imin = itemp; // update min if necessary
tempI += itemp; // add current sample to running sum
}
tempI = tempI/n *vref/0.8; // compute average we just took...
if (gui) uart.printf("=> %5.3f ", tempI);
if (statistics && gui) uart.printf("[%5.3f/%5.3f] ", imin*vref/0.8, imax*vref/0.8);
// if current is below this threshold, use LOW1 to measure...
if (tempI < 0.060) {
if (!gui) uart.printf("... too Low: %f A, switching to low1 ==>\r\n", tempI);
tempI=0;
enableLow1Range(); // change FETs to enable LOW1 measurement...
imin = 1.0; imax = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
itemp = LOW1_ADC; // read LOW1 sense amp output
if (statistics && itemp>imax) imax = itemp; // update max if necessary
if (statistics && itemp<imin) imin = itemp; // update min if necessary
tempI += itemp; // add current sample to running sum
}
tempI = tempI/n *vref/0.05/1000; // compute average we just took...
if (gui) uart.printf("%6.4f ", tempI);
if (statistics && gui) uart.printf("[%6.4f/%6.4f] ", imin*vref/0.05/1000, imax*vref/0.05/1000);
// if current is below this threshold, use LOW2 to measure...
if (tempI < 0.0009){
if (!gui) uart.printf("... too Low: %f A, switching to low2 ==>\r\n", tempI);
tempI=0;
enableLow2Range(); // change FETs to enable LOW1 measurement...
imin = 1.0; imax = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
itemp = LOW2_ADC; // read LOW2 sense amp output
if (statistics && itemp>imax) imax = itemp; // update max if necessary
if (statistics && itemp<imin) imin = itemp; // update min if necessary
tempI += itemp; // add current sample to running sum
}
tempI = tempI/n *vref/2/1000; // compute average we just took...
if (gui) uart.printf("%8.6f ", tempI);
if (statistics && gui) uart.printf("[%8.6f/%8.6f] ", imin*vref/2/1000, imax*vref/2/1000);
}
}
t.stop(); // stop the timer to see how long it took do do this...
enableHighRange();
if (!gui) uart.printf("\r\nCurrent = %f A Current Measure Time = %f sec\r\n", tempI, t.read());
}
// the autoranging should really be done with functions that return values, as should the
// functions below... This would make for shorter and more elegant code, but the author
// is a bit of a pasta programmer...
void measureHigh(){
float highI=0;
enableHighRange();
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
highI += HIGH_ADC;
}
highI = highI/n;
uart.printf("HIghI = %f A\r\n", vref*highI/0.8);
}
void measureLow1(){
float low1I=0;
enableLow1Range();
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
low1I += LOW1_ADC;
}
enableHighRange();
low1I = low1I/n;
uart.printf("low1I = %f A\r\n", vref*low1I/0.05/1000);
}
void measureLow2(){
float low2I=0;
enableLow2Range();
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
low2I += LOW2_ADC;
}
enableHighRange();
low2I = low2I/n;
uart.printf("low2I = %f A\r\n", vref*low2I/2/1000);
}
// measure the rail voltage, default being with
// a divide by 2 resistor divider
// It has to be switched out when not in use or it will
// add to the measured current, at least in the low ranges...
void measureRailV(){
float railv=0;
float mult = vref*2; // since divide by 2, we can measure up to 6.6V...
float vmin = 5; float vmax = 0;
float vtemp;
enableRailV(); // switch FETs so divider is connected...
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
vtemp = VRAIL_ADC; // read voltage at divider output...
if (statistics && vtemp>vmax) vmax = vtemp; // update max if necessary
if (statistics && vtemp<vmin) vmin = vtemp; // update min if necessary
railv += vtemp; // add current sample to running sum
}
disableRailV(); // now disconnect the voltage divider
railv = railv/n; // compute average (note this is in normalized ADC [0..1])
// Convert to voltage by multiplying by "mult"
if (!gui) uart.printf("RailV = %5.3f V ", mult*railv);
if (gui) uart.printf("%5.3f ", mult*railv);
if (statistics && gui) uart.printf("[%5.3f/%5.3f] ", mult*vmin, mult*vmax);
uart.printf("\r\n");
}
// not sure how useful this function is...
void measureAll(){
measureHigh();
measureLow1();
measureLow2();
measureRailV();
}
// test function to see if trigger pin is being hit...
// intended for use later to do timed triggering of measurements...
void triggerIn(){
uart.printf("You're triggering me! \r\n");
measureAll();
}
// main...
int main()
{
// set up basic conditions...
Timer m;
uart.baud(115200);
enableHighRange(); // default state - only HIGH sense amp in circuit, no divider
// signal that we're alive...
uart.printf("Hello World!\r\n");
// configure the trigger interrupt...
trigger.rise(&triggerIn);
while (true) {
count++;
wait(delay);
if (repeat){ // if repeat flag is set, keep making measurements...
m.reset(); // reset and start timer...
m.start();
measureAuto(); // measuring current using auto-ranging...
measureRailV(); // measure rail voltage...
m.stop(); // stop the timer.
if (!gui) uart.printf(" Total Measure Time = %f sec", m.read());
if (!gui) uart.printf("\r\n\r\n");
}
// see if there are any characters in the receive buffer...
// this is how we change things on the fly...
// Commands (single keystroke... it's easier)
// t = one shot automeasure
// v = measure volt
// h = one shot high measure
// k = one shot LOW1 measure
// l = one shot LOW2 measure (letter l)
// r = toggle repeat
// R = turn off repeat
// + = faster repeat rate
// - = slower repeat rate
// = = set repeat rate to 0.25 sec
// g = use human readable text output
// G = use compressed text format for GUI
// s = turn statistics output off
// S = turn statistics output on (only in GUI mode)
// n = decrease number of averages for each measurement
// N = increase number of averages for each measurement
//
// these were for testing FET switching...
// 1 = LOW_ENABLE = 0 (the number 1)
// 2 = LOW1 = 0
// 3 = LOW2 = 0
// 4 = VRAIL_MEAS = 0
// ! = LOW_ENABLE = 1
// @ = LOW1 = 1
// # = LOW2 = 1
// $ = VRAIL_MEAS = 1
if (uart.readable()){
temp = uart.getc();
if (temp==(int) 't') {
if (!gui) uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: ");
measureAuto();
measureRailV();
//measureAll();
}
if (temp==(int) 'v') {
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: ");
measureRailV();
}
if (temp==(int) 'h') {
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: ");
measureHigh();
}
if (temp==(int) 'k') {
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: ");
measureLow1();
}
if (temp==(int) 'l') {
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: ");
measureLow2();
}
if (temp==(int) '1') {
LOW_ENABLE = 0;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: LowEnable = %d\r\n", 0);
}
if (temp==(int) '2') {
LOW1 = 0;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: LOW1 = %d\r\n", 0);
}
if (temp==(int) '3') {
LOW2 = 0;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: LOW2 = %d\r\n", 0);
}
if (temp==(int) '4') {
VRAIL_MEAS = 0;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: VRAILMEAS = %d\r\n", 0);
}
if (temp==(int) '!') {
LOW_ENABLE = 1;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: LowEnable = %d\r\n", 1);
}
if (temp==(int) '@') {
LOW1 = 1;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: LOW1 = %d\r\n", 1);
}
if (temp==(int) '#') {
LOW2 = 1;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: LOW2 = %d\r\n", 1);
}
if (temp==(int) '$') {
VRAIL_MEAS = 1;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: VRAILMEAS = %d\r\n", 1);
}
if (temp==(int) 'r') {
repeat = !repeat;
uart.printf("Keyboard trigger: repeat toggle: %s \r\n", repeat ? "true" : "false");
}
if (temp==(int) 'R') repeat = false;
if (temp==(int) '+') {
delay -= 0.05;
if (delay<0.05) delay = 0.05;
}
if (temp==(int) '-') {
delay += 0.05;
if (delay>1) delay = 1;
}
if (temp==(int) '=') delay = 0.25;
if (temp==(int) 'g') gui = false;
if (temp==(int) 'G') gui = true;
if (temp==(int) 's') statistics = false;
if (temp==(int) 'S') statistics = true;
if (temp==(int) 'n') {
n -= 25;
if (n<25) n = 25;
}
if (temp==(int) 'N') {
n += 25;
if (n>1000) n = 1000;
}
if (temp==(int) 'N' || temp==(int) 'n') uart.printf("/r/n/r/n Averages = %d \r\n\r\b", n);
}
}
}