- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- Wireless ConnectivityWireless Connectivity
- RFID / NFCRFID / NFC
- Advanced AnalogAdvanced Analog
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
- S32Z/E
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- Generative AI & LLMs
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
- RFID / NFC
- Advanced Analog
-
- NXP Tech Blogs
- Home
- :
- i.MX Processors
- :
- i.MX Processors Knowledge Base
- :
- U-Boot Migration Example
U-Boot Migration Example
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
U-Boot Migration Example
U-Boot Migration Example
1. INTRODUCTION:
This document explains the general and basic steps to customize U-Boot for your own board. The board used in this document it is a working and stable board, the UDOO board (http://udoo.org).
2. REQUIREMENTS:
- Install Yocto Project. See the Freescale Yocto Project User's Guide.
- Generate and install the meta-toolchain. Follow this great training to do so Yocto Training - HOME
- Generate core-image-minimal of L3.14.28 of FSL BSP obtained from https://www.freescale.com/webapp/Download?colCode=L3.14.28_1.0.0_iMX6QDLS_BUNDLE&appType=license&loc...
3. ADDING i.MX6 CUSTOM BOARD SUPPORT FOR U-BOOT.
This section follows the steps found in Chapter 1 of the i.MX6 BSP Porting Guide of the Yocto documentation (L3.14.28) https://www.freescale.com/webapp/Download?colCode=L3.14.28_1.0.0_LINUX_DOCS&location=null&fpsp=1&WT_... .
- Obtain U-Boot Source Code. After having installed Yocto project and generate a valid imx6 image, the U-Boot code should be located at <build directory>/tmp/work/<machine>-poky-linuxgnueabi/u-boot-imx/<version>/git.
- Prepare the Code. Choose a board as reference, this board should be as similar as possible to your custom board.
- Copy the board directory :
$ cp -R board/freescale/mx6sabresd/ board/freescale/mx6_udoo
- Copy the existing mx6sabresd.h configuration file as mx6_udoo.h
$ cp include/configs/mx6sabresd.h include/configs/mx6_udoo.h
- Create one entry in boards.cfg. Add a configuration entry in the boards.cfg file.
Active arm armv7 mx6 freescale mx6_udoo mx6_udoo mx6_udoo:IMX_CONFIG=board/freescale/mx6_udoo/mx6dl_4x_mt41j128.cfg,MX6Q,DEFAULT_FDT_FILE="imx6q-udoo.dtb",DDR_MB=1024
- Rename <board>.c file. Rename board/freescale/mx6sabresd/mx6sabresd.c to board/freescale/mx6_udoo/mx6_udoo.c
- Modify Makefile. Change the line of COBJS to your custom board at board/freescale/mx6_udoo/:
obj-y := mx6sabresd.o
- Create a Shell script. Create a script to compile your new configuration. The script for this example is shown below and its name is build_u-boot.sh:
#!/bin/bash
export ARCH=arm
export CROSS_COMPILE=/opt/poky/1.7/sysroots/x86_64-pokysdk-linux/usr/bin/arm-poky-linux-gnueabi/arm-poky-linux-gnueabi-
make distclean;
make mx6_udoo_config
make
- Run the script to verify if the new configuration is correct.
$./build_u-boot.sh
4. CUSTOMIZING BOARD CODE
- The fist part to customize is the DCD table. The DCD table contains configuration data for the DDR controller and memory. The DCD is read by the BootROM code in the iMX family and executed before copying the Uboot image to DDR. The DCD is built in the .cfg file pointed in the new entry we just added in the boards.cfg file (mx6dl_4x_mt41j128.cfg).
Below you can find an example of the data that can be found in this file:
/*
* Device Configuration Data (DCD)
*
* Each entry must have the format:
* Addr-type Address Value
*
* where:
* Addr-type register length (1,2 or 4 bytes)
* Address absolute address of the register
* value value to be stored in the register
*/
DATA 4, 0x020e0774, 0x000C0000
DATA 4, 0x020e0754, 0x00000000
DATA 4, 0x020e04ac, 0x00000030
DATA 4, 0x020e04b0, 0x00000030
DATA 4, 0x020e0464, 0x00000030
DATA 4, 0x020e0490, 0x00000030
DATA 4, 0x020e074c, 0x00000030
DATA 4, 0x020e0494, 0x00000030
DATA 4, 0x020e04a0, 0x00000000
The .cfg files used in this example were taken from an old U-Boot version (2009) non dtb capable. The used files are found in the attached .zip file.
- The specific initialization code for each board is found in mx6<customer board>.c in board/freescale/mx6<customer board>.c in this case board/freescale/mx6_udoo/mx6_udoo.c file. Below it is explained the needed changes to route the serial console to the correct UART module, disable an external watchdog, configure and initialize the Ethernet PHY, change the lvds clock and configure the correct USDHC module.
U-Boot calls already defined functions from a function pointer array that takes care of the board initialization at different stages. For example the board_early_init_f() is called at an early phase where we can disable the wdog and initialize the uart pins; board_init() and board_late_init() are called after board_early_init_f().
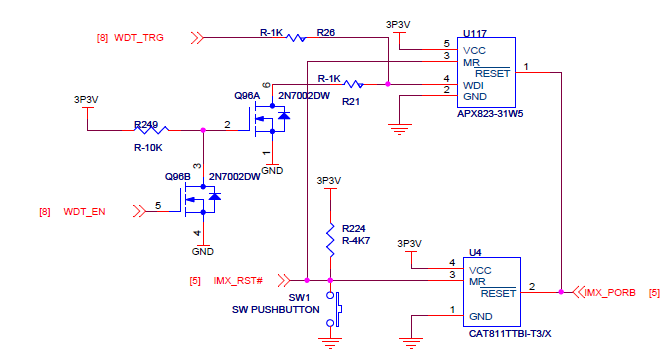
- The UDOO board features an external watchdog that needs to be disabled with a GPIO, otherwise U-Boot resets after a few seconds:
The WDOG pins need to be configured and in the mx6_udoo.c file a global struct configuration for those pins is declared, as well as macros for each pin
#define WDT_EN IMX_GPIO_NR(5, 4)
#define WDT_TRG IMX_GPIO_NR(3, 19)
iomux_v3_cfg_t const wdog_pads[] = {
MX6_PAD_EIM_A24__GPIO5_IO04 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_EIM_D19__GPIO3_IO19,
};
static void setup_iomux_wdog(void)
{
imx_iomux_v3_setup_multiple_pads(wdog_pads, ARRAY_SIZE(wdog_pads));
gpio_direction_output(WDT_TRG, 0);
gpio_direction_output(WDT_EN, 1);
gpio_direction_input(WDT_TRG);
}
This configuration needs to be called at some point of the board_early_init_f()
int board_early_init_f(void)
{
setup_iomux_wdog();
This way the board_early_init_f() calls the iomux for the external wdog and disables it.
- The UART console is routed to UART2, EIM_D26/UART2_TXD and EIM_D27/UART2_RXD. A different structure is defined with the pin configuration for the UART2.

iomux_v3_cfg_t const uart2_pads[] = {
MX6_PAD_EIM_D26__UART2_TX_DATA | MUX_PAD_CTRL(UART_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_EIM_D27__UART2_RX_DATA | MUX_PAD_CTRL(UART_PAD_CTRL),
};
This configuration should be called at early stage too.
static void setup_iomux_uart(void)
{
imx_iomux_v3_setup_multiple_pads(uart2_pads, ARRAY_SIZE(uart2_pads));
}
int board_early_init_f(void)
{
setup_iomux_wdog();
setup_iomux_uart();
Also the UART BASE register has to be defined as well as the console device. This is defined in the include/configs/mx6_udoo.h file.
#define CONFIG_MXC_UART_BASE UART2_BASE
#define CONFIG_CONSOLE_DEV "ttymxc1"
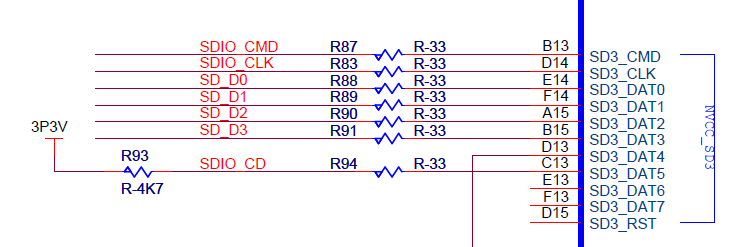
- The UDOO board features only one micro SD slot to boot and U-Boot environment storage. It uses only 4 bits and it has to be configured too. In the include/configs/mx6_udoo.h file the USDHC module has to be defined and the MMC environment device.
#define CONFIG_SYS_FSL_USDHC_NUM 3
#define CONFIG_SYS_MMC_ENV_DEV 0 /* SDHC3 */
The USDHC3 pin configuration has to be defined:
iomux_v3_cfg_t const usdhc3_pads[] = {
MX6_PAD_SD3_CLK__SD3_CLK | MUX_PAD_CTRL(USDHC_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_SD3_CMD__SD3_CMD | MUX_PAD_CTRL(USDHC_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_SD3_DAT0__SD3_DATA0 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(USDHC_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_SD3_DAT1__SD3_DATA1 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(USDHC_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_SD3_DAT2__SD3_DATA2 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(USDHC_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_SD3_DAT3__SD3_DATA3 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(USDHC_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_NANDF_D0__GPIO2_IO00 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL), /* CD */
};
struct fsl_esdhc_cfg usdhc_cfg[1] = {
{USDHC3_BASE_ADDR, 0, 4},
};
This must be called and configured from the board_mmc_init() function:
int board_mmc_init(bd_t *bis)
{
s32 status = 0;
imx_iomux_v3_setup_multiple_pads(
usdhc3_pads, ARRAY_SIZE(usdhc3_pads));
usdhc_cfg[0].sdhc_clk = mxc_get_clock(MXC_ESDHC3_CLK);
status |= fsl_esdhc_initialize(bis, &usdhc_cfg[0]);
return status;
}
- The Ethernet PHY is configured in the board_eth_init() function. This function should initialize the pins for the external ethernet phy, mdio and phy configuration. Just a piece of code is shown below:
iomux_v3_cfg_t const enet_pads1[] = {
MX6_PAD_ENET_MDIO__ENET_MDIO | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_ENET_MDC__ENET_MDC | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_TXC__RGMII_TXC | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_TD0__RGMII_TD0 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_TD1__RGMII_TD1 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_TD2__RGMII_TD2 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_TD3__RGMII_TD3 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_TX_CTL__RGMII_TX_CTL | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_ENET_REF_CLK__ENET_TX_CLK | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RXC__RGMII_RXC | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
/* RGMII reset */
MX6_PAD_EIM_D23__GPIO3_IO23 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL),
/* alimentazione ethernet*/
MX6_PAD_EIM_EB3__GPIO2_IO31 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL),
/* pin 32 - 1 - (MODE0) all */
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RD0__GPIO6_IO25 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL),
/* pin 31 - 1 - (MODE1) all */
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RD1__GPIO6_IO27 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL),
/* pin 28 - 1 - (MODE2) all */
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RD2__GPIO6_IO28 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL),
/* pin 27 - 1 - (MODE3) all */
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RD3__GPIO6_IO29 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL),
/* pin 33 - 1 - (CLK125_EN) 125Mhz clockout enabled */
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RX_CTL__GPIO6_IO24 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(NO_PAD_CTRL),
};
static iomux_v3_cfg_t const enet_pads2[] = {
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RD0__RGMII_RD0 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RD1__RGMII_RD1 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RD2__RGMII_RD2 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RD3__RGMII_RD3 | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
MX6_PAD_RGMII_RX_CTL__RGMII_RX_CTL | MUX_PAD_CTRL(ENET_PAD_CTRL),
};
static void setup_iomux_enet(void)
{
imx_iomux_v3_setup_multiple_pads(enet_pads1, ARRAY_SIZE(enet_pads1));
udelay(20);
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(2, 31), 1); /* Power on enet */
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(3, 23), 0); /* assert PHY rst */
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 24), 1);
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 25), 1);
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 27), 1);
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 28), 1);
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 29), 1);
udelay(1000);
gpio_set_value(IMX_GPIO_NR(3, 23), 1); /* deassert PHY rst */
/* Need delay 100ms to exit from reset. */
udelay(1000 * 100);
gpio_free(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 24));
gpio_free(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 25));
gpio_free(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 27));
gpio_free(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 28));
gpio_free(IMX_GPIO_NR(6, 29));
imx_iomux_v3_setup_multiple_pads(enet_pads2, ARRAY_SIZE(enet_pads2));
}
Let's notice that the external PHY is not the same as the SABRESD AR8031. The UDOO features the MICREL KSZ9031 PHY. The latter needs to be defined and the former undefined in the include/configs/mx6_udoo.h file.
#undef CONFIG_PHY_ATHEROS
#define CONFIG_PHY_MICREL
#define CONFIG_PHY_MICREL_KSZ9031
Besides the PHY address has to be changed.
#define CONFIG_FEC_MXC_PHYADDR 6
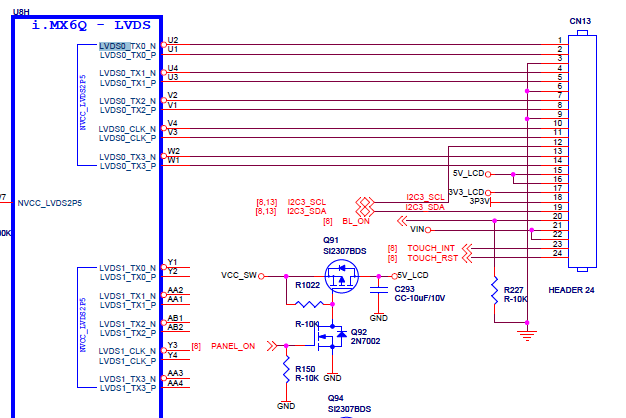
- At this point, the serial console, SD card saving arguments and ethernet should be working. The last point is to configure the LVDS display. The LVDS display of the UDOO board is connected in the same port as the SABRE-SD board, but the operation frequency is different and it has to be modified to work at ~ 33.26MHz for the 7 inches LVDS display.
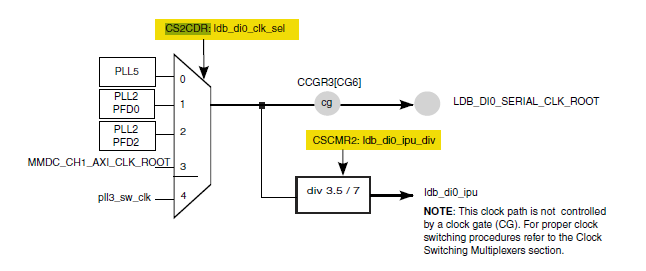
The mx6_udoo.c file contains a setup_display function that configures the LDB module. This functions is called in the board_early_init_f(). With the current clock configuration is not possible to get the 33.2MHz for the LVDS and a different clock source for the LDB module must be chosen. The backlight and lvds power signals must be on.
The current configuration uses the mmdc_ch1 clock and to get closer to 33.26MHz the PLL2_PFD0 is chosen.
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(1, 2), 1); /* LVDS power On */
gpio_direction_output(IMX_GPIO_NR(1, 4), 1); /* LVDS backlight On */
imx_iomux_v3_setup_multiple_pads(di0_pads, ARRAY_SIZE(di0_pads));
enable_ipu_clock();
imx_setup_hdmi();
/* Turn on4LDB0, LDB1, IPU,IPU DI0 clocks */
reg = readl(&mxc_ccm->CCGR3);
reg |= MXC_CCM_CCGR3_LDB_DI0_MASK | MXC_CCM_CCGR3_LDB_DI1_MASK;
writel(reg, &mxc_ccm->CCGR3);
/* set LDB0, LDB1 clk select to 011/011 */
reg = readl(&mxc_ccm->cs2cdr);
reg &= ~(MXC_CCM_CS2CDR_LDB_DI0_CLK_SEL_MASK
| MXC_CCM_CS2CDR_LDB_DI1_CLK_SEL_MASK);
reg |= (1 << MXC_CCM_CS2CDR_LDB_DI0_CLK_SEL_OFFSET)
| (1 << MXC_CCM_CS2CDR_LDB_DI1_CLK_SEL_OFFSET);
writel(reg, &mxc_ccm->cs2cdr);
With this changes you can compile the new U-Boot image with ./build_u-boot.sh and then just copy the uboot.imx file to your sd:
# sudo cp if=uboot.imx of=/dev/sdX bs=512 seek= 2 && sync
5. TESTING YOUR CHANGES
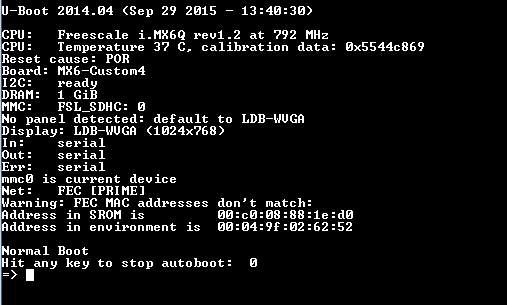
Inser the sd with the U-Boot image to micro sd slot and power up the board. You should get the U-Boot serial console like shown below.
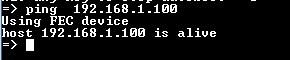
In the console you can test the ethernet and phy configuration with the PING command:
I hope you find these basic steps useful for different boards.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
Thank you for this valuable information.
Does the iomux in kernel (from device tree) shall override the iomux in u-boot ?
Regards,
Ran
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Can you give the solution for below screenshots