- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- Wireless Connectivity
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- MCUXpresso Training Hub
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
-
- Home
- :
- NXP Tech Blog
- :
- SPDK_on_Layerscape
SPDK_on_Layerscape
SPDK_on_Layerscape
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
SPDK on Layerscape
SPDK (Storage Performance Development Kit) is an optimized storage reference architecture. It is initiated and developed by Intel.
SPDK provides a set of tools and libraries for writing high performance, scalable, user-mode storage applications. It achieves high performance by moving all of the necessary drivers into userspace and operating in a polled mode, like DPDK.
Background
- Hard drive latency is dramatically dropping down: HDD(SAS/SATA) ~10ms → SSD (SATA) ~0.1ms → SSD (NVMe) ~0.075ms
- Bus width and command queue is increasing: SAS/SATA 6Gbps, 32 commands/queue → NVMe 24Gbps, 64k commands/queue
- Network bandwidth is increasing: 1Gbps → 10Gbps → 40Gbps → 100Gbps
All these changes make software latency the major contributor to the whole latency stack in nowadays.
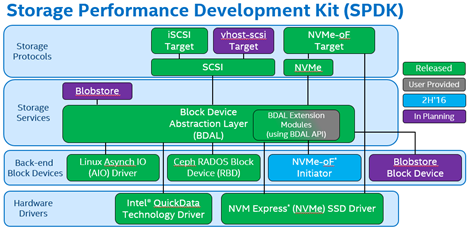
Architecture and subcomponents
Two key changes for SPDK to reduce latency caused by software stack:
- Poll mode driver: Submits the request for a read or write, and then goes off to do other work, checking back at some interval to see if the I/O has yet been completed. This avoids the latency and overhead of using interrupts and allows the application to improve I/O efficiency
- User space data process: Avoiding the kernel context switches and interrupts saves a significant amount of processing overhead, allowing more cycles to be spent doing the actual storing of the data.
Following is the software stack of SPDK:
Subcomponents
NVMe Driver
lib/nvme
Provides direct, zero-copy data transfer to and from NVMe SSDs. It controls NVMe devices by directly mapping the PCI BAR into the local process and performing MMIO. I/O is submitted asynchronously via queue pairs.
NVMe over Fabrics Target
lib/nvmf
User space application that presents block devices over the network using RDMA. It requires an RDMA-capable NIC with its corresponding OFED software package installed to run.
iSCSI Target
lib/iscsi
Implementation of the established specification for block traffic over Ethernet. Current version uses the kernel TCP/IP stack by default.
Block Device Abstraction Layer
lib/bdev
This generic block device abstraction is the glue that connects the storage protocols to the various device drivers and block devices. Also provides flexible APIs for additional customer functionality (RAID, compression, dedup, and so on) in the block layer.
It defines:
- a driver module API for implementing bdev drivers
- an application API for enumerating and claiming SPDK block devices and performance operations
- bdev drivers for NVMe, malloc (ramdisk), Linux AIO and Ceph RBD
Blobstore
lib/blob
A persistent, power-fail safe block allocator designed to be used as the local storage system backing a higher level storage service, typically in lieu of a traditional filesystem.
This is a virtual device that VMs or databases could interact with.
BlobFS
lib/blobfs
Adds basic filesystem functionality like filenames on top of the blobstore.
vhost
lib/vhost
It extends SPDK to present virtio storage controllers to QEMU-based VMs and process I/O submitted to devices attached to those controllers
Event framework
lib/event
A framework for writing asynchronous, polled-mode, shared-nothing server applications.
The event framework is intended to be optional; most other SPDK components are designed to be integrated into an application without specifically depending on the SPDK event library. The framework defines several concepts - reactors, events, and pollers.
Build and Test
General guides can be found here and here.
SPDK build/deployment is tested on LS2088.
Environment Setup
SW
- OS: Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS
- SPDK: 43727fb7e5c@master branch
- DPDK: 18.11
HW
- LS2088A-RDB platform
- INTEL SSDPED1D280GA NVMe SSD card with firmware version of E2010325
Build
DPDK
# git clone git://dpdk.org/dpdk
# export RTE_TARGET=arm64-dpaa2-linuxapp-gcc
# export RTE_SDK=/code/dpdk
# make T=arm64-dpaa-linuxapp-gcc CONFIG_RTE_KNI_KMOD=n CONFIG_RTE_LIBRTE_PPFE_PMD=n
CONFIG_RTE_EAL_IGB_UIO=n install -j 4
SPDK
# git clone https://github.com/spdk/spdk
# cd spdk
# sudo ./scripts/pkgdep.sh
#./configure –with-dpdk=/code/dpdk/arm64-dpaa2-linuxapp-gcc
# make -j8
Deploy
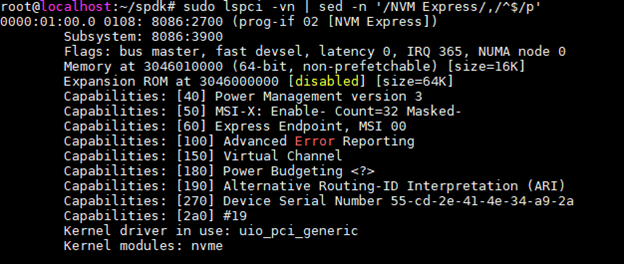
check NVMe status
# sudo lspci -vn | sed -n '/NVM Express/,/^$/p'
You should see lines like
Deploy SPDK
UIO
# modprobe uio
# modprobe uio_pci_generic
# echo -n "8086 2700 8086 3900" > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/uio_pci_generic/new_id
# echo -n "0000:01:00.0" > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/nvme/unbind
# echo -n "0000:01:00.0" > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/uio_pci_generic/bind
VFIO
# modprobe vfio-pci
# cd <SPDK_ROOT_DIR>
# ./scripts/setup.sh
Test
# sudo ./examples/nvme/identify/identify
This app should give you the detail disk info of attached NVMe storage.
# sudo ./examples/nvme/perf/perf -q 128 -s 4096 -w write -t 60 -c 0xFF -o 2048 -r 'trtype:PCIe traddr:0000:01:00.0'
This will give SPDK performance data.
With prior described HW/SW settings, following data are achieved (performance in MBps):
|
|
512B |
2K |
4K |
8K |
|
Rd |
286 |
1082 |
1120 |
1461 |
|
Wr |
117 |
458 |
1445 |
1137 |
Benchmark
FIO
Build FIO with SPDK
# git clone https://github.com/axboe/fio --branch fio-3.3
# cd fio
# make
Build SPDK with FIO plugin support
# cd spdk
# ./configure --with-fio=<path-to-fio-src> --enable-debug
# make DPDK_CONFIG=arm64-armv8a-linuxapp-gcc
Run FIO
# cd fio
# LD_PRELOAD=../spdk/examples/nvme/fio_plugin/fio_plugin ./fio --name=nvme --numjobs=1
--filename="trtype=PCIe traddr=0000.01.00.0 ns=1" --bs=4K --iodepth=1
--ioengine=../spdk/examples/nvme/fio_plugin/fio_plugin --direct=1 --sync=0 --norandommap --group_reporting
--size=10% --runtime=3 -rwmixwrite=30 --thread=1 --rw=r
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
101
6 -
communication standards
4 -
General Purpose Microcontrollers
23 -
i.MX RT Processors
46 -
i.MX Processors
49 -
Interface
1 -
introduction
13 -
LPC Microcontrollers
73 -
MCUXpresso
34 -
MCUXpresso Secure Provisioning Tool
1 -
MCUXpresso Conig Tools
30 -
MCUXpresso IDE
42 -
MCUXpresso SDK
26 -
Model-Based Design Toolbox
6 -
MQX Software Solutions
2 -
QorIQ Processing Platforms
1 -
QorIQ Devices
5 -
S32N Processors
4 -
S32Z|E Processors
6 -
SW | Downloads
7 -
日本語ブログ
5
- « Previous
- Next »