- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- Wireless ConnectivityWireless Connectivity
- RFID / NFCRFID / NFC
- Advanced AnalogAdvanced Analog
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
- S32Z/E
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- Generative AI & LLMs
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
- RFID / NFC
- Advanced Analog
-
- NXP Tech Blogs
lpc1768 as a USB listener
I'm working with an LPC1768(FBD100) and need to connect to a PC through a serial USB. As a starting point, I used the sample package USB virtual com port.
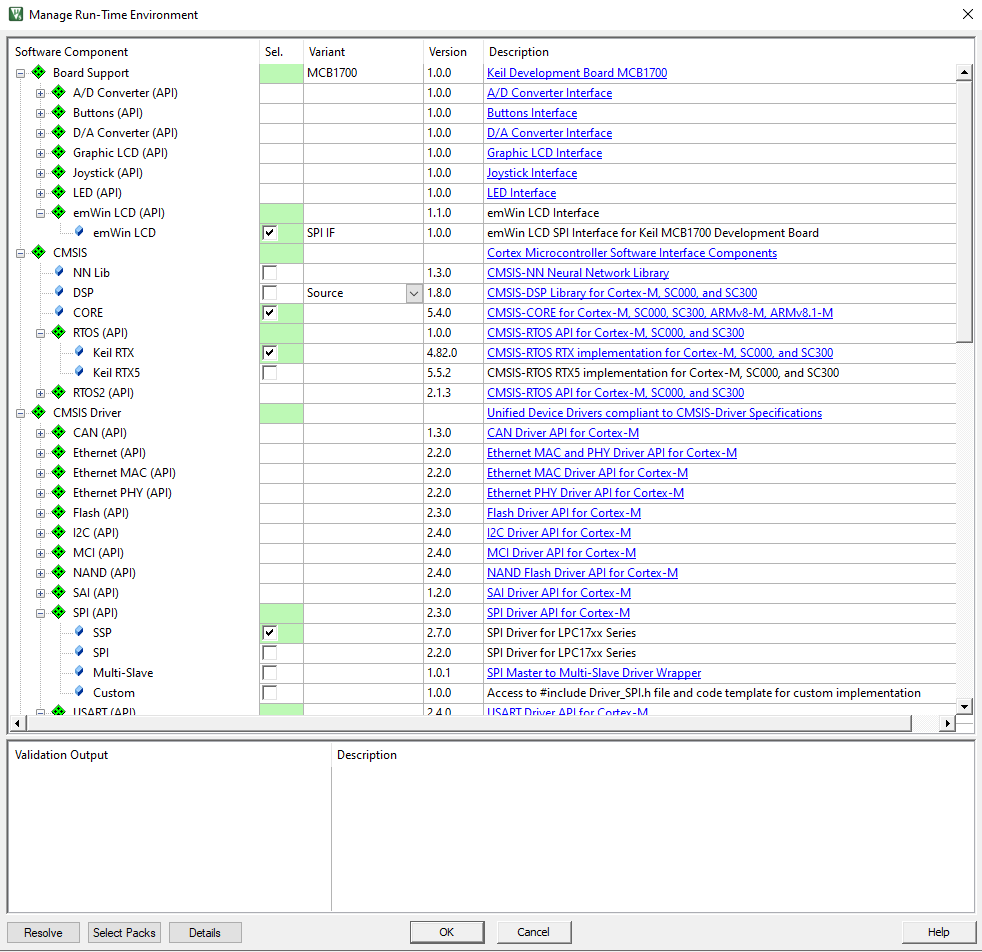
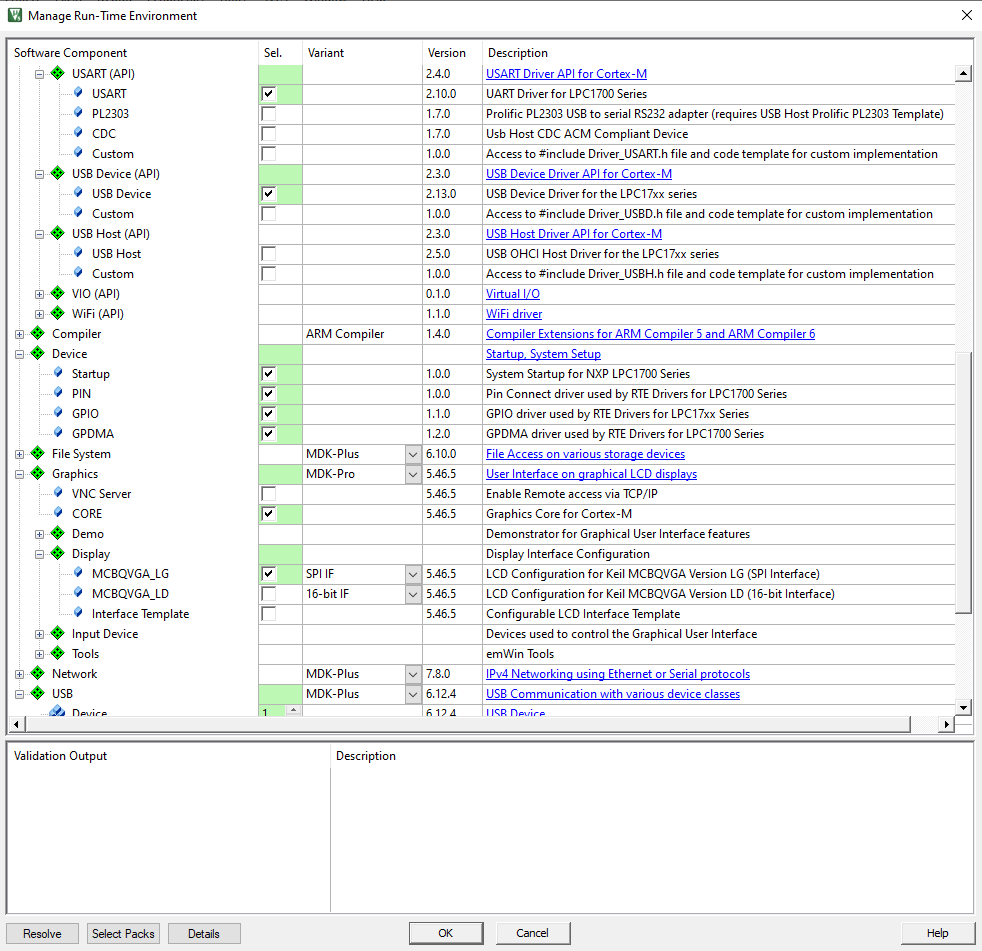
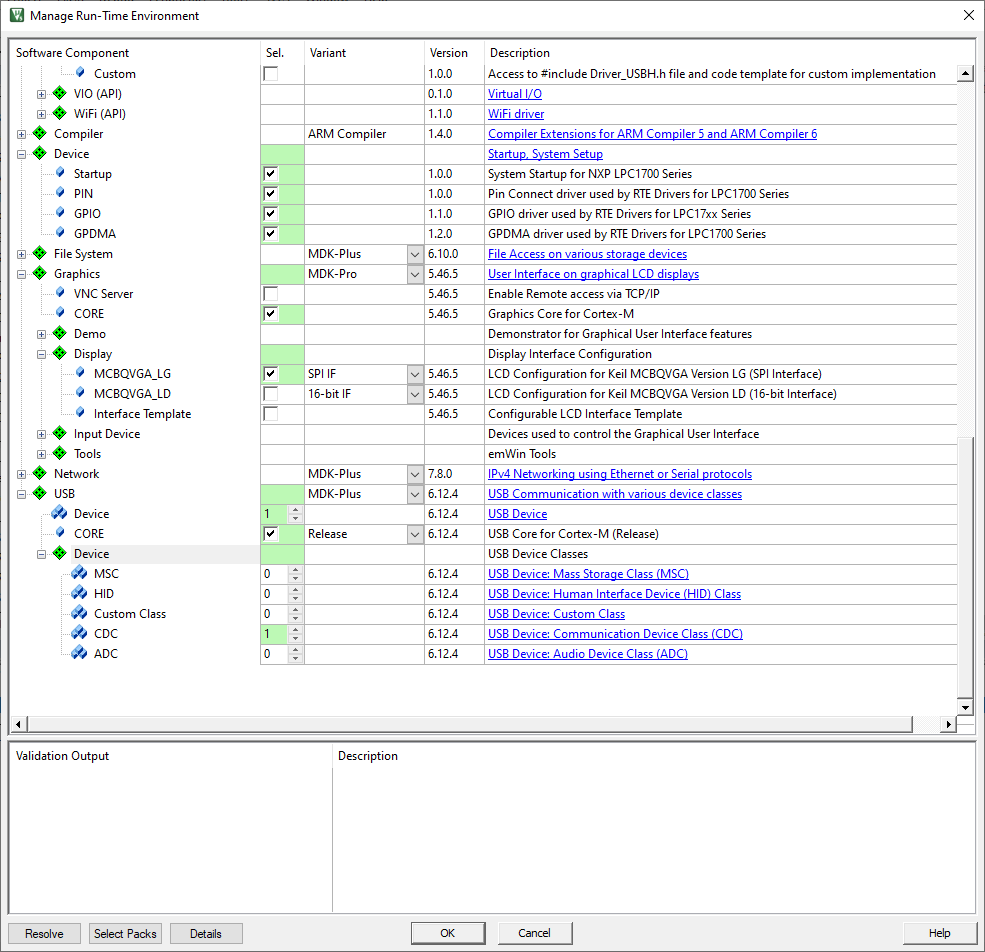
Installed packages:
My code:
[code]
#include "includes.h"
int main (void) {
MenuEntryVType* MenuEntry;
GUI_Init();
WM_SetCreateFlags(WM_CF_MEMDEV);
FRAMEWIN_SetDefaultSkinClassic();
PROGBAR_SetDefaultSkinClassic();
SCROLLBAR_SetDefaultSkinClassic();
FRAMEWIN_SetDefaultFont(StdFont);
InitOutputs();
InitADCs();
InitDAC();
InitPWM(100);
InitI2C();
GetConfig();
osDelay(1500);
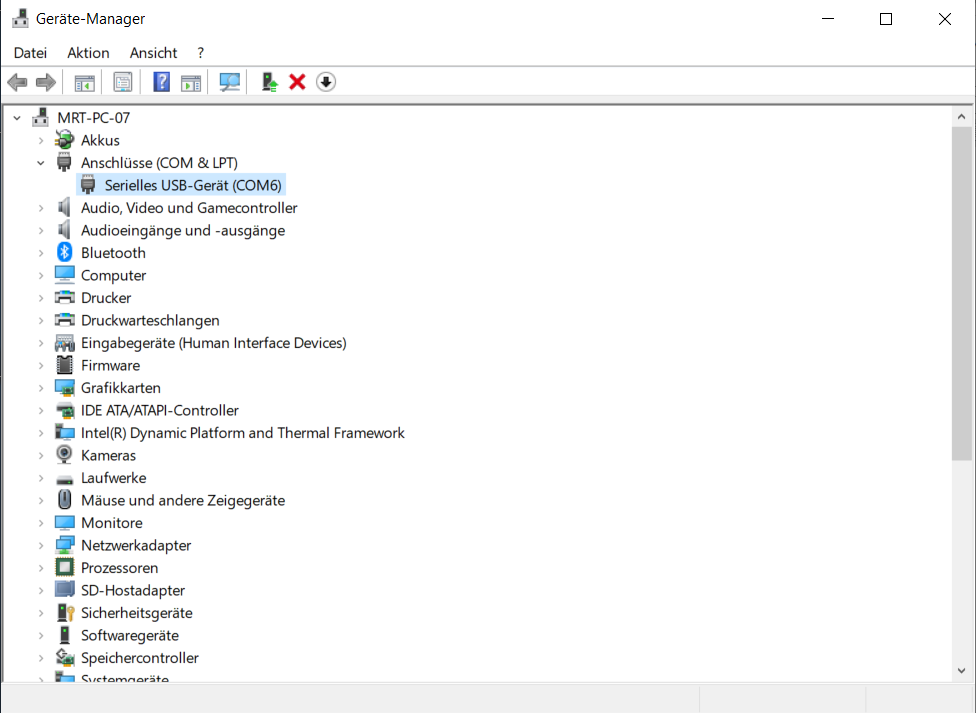
// Works as expected ; new COMx device shows in dev manager.
USBD_Initialize (0U); // USB Device 0 Initialization
USBD_Connect (0U); // USB Device 0 Connect
// menu handling code
// actual functionality start servos, etc.)
// does not get executed. Why?
return 0;
}
[/code]
Why does USBD_Connect() hang? no code gets executed past that point; the device does connect, however, to the PC:
rl_usb.h contains the definitions of USBD_Initialize() and USBD_Connect():
[code]
/// \brief Initialize USB Device stack and controller
/// \param[in] device index of USB Device.
/// \return status code that indicates the execution status of the function as defined with \ref usbStatus.
extern usbStatus USBD_Initialize (uint8_t device);
/// \brief Activate pull-up on D+ or D- line to signal USB Device connection on USB Bus
/// \param[in] device index of USB Device.
/// \return status code that indicates the execution status of the function as defined with \ref usbStatus.
extern usbStatus USBD_Connect (uint8_t device);
[/code]
These are function declarations; I don't know where the implementations are (likely in USB_CM3_L.lib).
Read/write functions are defined in USBD_User_CDC_ACM_UART_0.c
[code]
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* MDK Middleware - Component ::USB:Device
* Copyright (c) 2004-2019 ARM Germany GmbH. All rights reserved.
*------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Name: USBD_User_CDC_ACM_UART_0.c
* Purpose: USB Device Communication Device Class (CDC)
* Abstract Control Model (ACM) USB <-> UART Bridge User module
* Rev.: V1.0.3
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* \addtogroup usbd_cdcFunctions
*
* USBD_User_CDC_ACM_UART_0.c implements the application specific
* functionality of the CDC ACM class and is used to demonstrate a USB <-> UART
* bridge. All data received on USB is transmitted on UART and all data
* received on UART is transmitted on USB.
*
* Details of operation:
* UART -> USB:
* Initial reception on UART is started after the USB Host sets line coding
* with SetLineCoding command. Having received a full UART buffer, any
* new reception is restarted on the same buffer. Any data received on
* the UART is sent over USB using the CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread thread.
* USB -> UART:
* While the UART transmit is not busy, data transmission on the UART is
* started in the USBD_CDC0_ACM_DataReceived callback as soon as data is
* received on the USB. Further data received on USB is transmitted on
* UART in the UART callback routine until there is no more data available.
* In this case, the next UART transmit is restarted from the
* USBD_CDC0_ACM_DataReceived callback as soon as new data is received
* on the USB.
*
* The following constants in this module affect the module functionality:
*
* - UART_PORT: specifies UART Port
* default value: 0 (=UART0)
* - UART_BUFFER_SIZE: specifies UART data Buffer Size
* default value: 512
*
* Notes:
* If the USB is slower than the UART, data can get lost. This may happen
* when USB is pausing during data reception because of the USB Host being
* too loaded with other tasks and not polling the Bulk IN Endpoint often
* enough (up to 2 seconds of gap in polling Bulk IN Endpoint may occur).
* This problem can be solved by using a large enough UART buffer to
* compensate up to a few seconds of received UART data or by using UART
* flow control.
* If the device that receives the UART data (usually a PC) is too loaded
* with other tasks it can also loose UART data. This problem can only be
* solved by using UART flow control.
*
* This file has to be adapted in case of UART flow control usage.
*/
//! [code_USBD_User_CDC_ACM]
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "rl_usb.h"
#
if defined(RTE_CMSIS_RTOS2)#include "cmsis_os2.h"
#
if defined(RTE_CMSIS_RTOS2_RTX5)#include "rtx_os.h"
# endif# endif#
if defined(RTE_CMSIS_RTOS)#include "cmsis_os.h"
# endif
#include "Driver_USART.h"
// UART Configuration ----------------------------------------------------------
# define UART_PORT 1 // UART Port number
# define UART_BUFFER_SIZE 512 // UART Buffer Size
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# define _UART_Driver_(n) Driver_USART## n# define UART_Driver_(n) _UART_Driver_(n)
extern ARM_DRIVER_USART UART_Driver_(UART_PORT);#
define ptrUART( & UART_Driver_(UART_PORT))
// External functions
# ifdef USB_CMSIS_RTOS
extern void CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread(void
const * arg) __attribute((noreturn));#
endif
// Local Variables
static uint8_t uart_rx_buf[UART_BUFFER_SIZE];
static uint8_t uart_tx_buf[UART_BUFFER_SIZE];
static volatile int32_t uart_rx_cnt = 0;
static volatile int32_t usb_tx_cnt = 0;
static void * cdc_acm_bridge_tid = 0 U;
static CDC_LINE_CODING cdc_acm_line_coding = {
0 U,
0 U,
0 U,
0 U
};
// Called when UART has transmitted or received requested number of bytes.
// \param[in] event UART event
// - ARM_USART_EVENT_SEND_COMPLETE: all requested data was sent
// - ARM_USART_EVENT_RECEIVE_COMPLETE: all requested data was received
static void UART_Callback(uint32_t event) {
int32_t cnt;
if (event & ARM_USART_EVENT_SEND_COMPLETE) {
// USB -> UART
cnt = USBD_CDC_ACM_ReadData(0 U, uart_tx_buf, UART_BUFFER_SIZE);
if (cnt > 0) {
ptrUART - > Send(uart_tx_buf, (uint32_t)(cnt));
}
}
if (event & ARM_USART_EVENT_RECEIVE_COMPLETE) {
// UART data received, restart new reception
uart_rx_cnt += UART_BUFFER_SIZE;
ptrUART - > Receive(uart_rx_buf, UART_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
}
// Thread: Sends data received on UART to USB
// \param[in] arg not used.
# ifdef USB_CMSIS_RTOS2
__NO_RETURN static void CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread(void * arg) {
#
else
__NO_RETURN void CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread(void
const * arg) {
#
endif
int32_t cnt, cnt_to_wrap;
(void)(arg);
while (1) {
// UART - > USB
if (ptrUART - > GetStatus().rx_busy != 0 U) {
cnt = uart_rx_cnt;
cnt += ptrUART - > GetRxCount();
cnt -= usb_tx_cnt;
if (cnt >= UART_BUFFER_SIZE) {
// Dump data received on UART if USB is not consuming fast enough
usb_tx_cnt += cnt;
cnt = 0 U;
}
if (cnt > 0) {
cnt_to_wrap = (int32_t)(UART_BUFFER_SIZE - ((uint32_t) usb_tx_cnt & (UART_BUFFER_SIZE - 1)));
if (cnt > cnt_to_wrap) {
cnt = cnt_to_wrap;
}
cnt = USBD_CDC_ACM_WriteData(0 U, (uart_rx_buf + ((uint32_t) usb_tx_cnt & (UART_BUFFER_SIZE - 1))), cnt);
if (cnt > 0) {
usb_tx_cnt += cnt;
}
}
}
osDelay(10 U);
}
}#
ifdef USB_CMSIS_RTOS2# ifdef USB_CMSIS_RTOS2_RTX5
static osRtxThread_t cdc0_acm_uart_to_usb_thread_cb_mem __SECTION(.bss.os.thread.cb);
static uint64_t cdc0_acm_uart_to_usb_thread_stack_mem[512 U / 8 U] __SECTION(.bss.os.thread.stack);#
endif
static
const osThreadAttr_t cdc0_acm_uart_to_usb_thread_attr = {
"CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread",
0 U,
#ifdef USB_CMSIS_RTOS2_RTX5 &
cdc0_acm_uart_to_usb_thread_cb_mem,
sizeof(osRtxThread_t),
&
cdc0_acm_uart_to_usb_thread_stack_mem[0],
#
else
NULL,
0 U,
NULL,
#endif
512 U,
osPriorityNormal,
0 U,
0 U
};#
else
extern
const osThreadDef_t os_thread_def_CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread;
osThreadDef(CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread, osPriorityNormal, 1 U, 0 U);#
endif
[/code]
// CDC ACM Callbacks -----------------------------------------------------------
// Called when new data was received from the USB Host.
// \param[in] len number of bytes available to read.
void USBD_CDC0_ACM_DataReceived(uint32_t len) {
int32_t cnt;
(void)(len);
if (ptrUART - > GetStatus().tx_busy == 0 U) {
// Start USB -> UART
cnt = USBD_CDC_ACM_ReadData(0 U, uart_tx_buf, UART_BUFFER_SIZE);
if (cnt > 0) {
ptrUART - > Send(uart_tx_buf, (uint32_t)(cnt));
}
}
}
// Called during USBD_Initialize to initialize the USB CDC class instance (ACM).
void USBD_CDC0_ACM_Initialize(void) {
ptrUART - > Initialize(UART_Callback);
ptrUART - > PowerControl(ARM_POWER_FULL);
#
ifdef USB_CMSIS_RTOS2
cdc_acm_bridge_tid = osThreadNew(CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread, NULL, & cdc0_acm_uart_to_usb_thread_attr);#
else
cdc_acm_bridge_tid = osThreadCreate(osThread(CDC0_ACM_UART_to_USB_Thread), NULL);#
endif
}
// Called during USBD_Uninitialize to de-initialize the USB CDC class instance (ACM).
void USBD_CDC0_ACM_Uninitialize(void) {
if (osThreadTerminate(cdc_acm_bridge_tid) == osOK) {
cdc_acm_bridge_tid = NULL;
}
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_ABORT_RECEIVE, 0 U);
ptrUART - > PowerControl(ARM_POWER_OFF);
ptrUART - > Uninitialize();
}
// Called upon USB Bus Reset Event.
void USBD_CDC0_ACM_Reset(void) {
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_ABORT_SEND, 0 U);
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_ABORT_RECEIVE, 0 U);
}
// Called upon USB Host request to change communication settings.
// \param[in] line_coding pointer to CDC_LINE_CODING structure.
// \return true set line coding request processed.
// \return false set line coding request not supported or not processed.
bool USBD_CDC0_ACM_SetLineCoding(const CDC_LINE_CODING * line_coding) {
uint32_t data_bits = 0 U, parity = 0 U, stop_bits = 0 U;
int32_t status;
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_ABORT_SEND, 0 U);
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_ABORT_RECEIVE, 0 U);
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_CONTROL_TX, 0 U);
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_CONTROL_RX, 0 U);
switch (line_coding - > bCharFormat) {
case 0: // 1 Stop bit
stop_bits = ARM_USART_STOP_BITS_1;
break;
case 1: // 1.5 Stop bits
stop_bits = ARM_USART_STOP_BITS_1_5;
break;
case 2: // 2 Stop bits
stop_bits = ARM_USART_STOP_BITS_2;
}
switch (line_coding - > bParityType) {
case 0: // None
parity = ARM_USART_PARITY_NONE;
break;
case 1: // Odd
parity = ARM_USART_PARITY_ODD;
break;
case 2: // Even
parity = ARM_USART_PARITY_EVEN;
break;
default:
return false;
}
switch (line_coding - > bDataBits) {
case 5:
data_bits = ARM_USART_DATA_BITS_5;
break;
case 6:
data_bits = ARM_USART_DATA_BITS_6;
break;
case 7:
data_bits = ARM_USART_DATA_BITS_7;
break;
case 8:
data_bits = ARM_USART_DATA_BITS_8;
break;
default:
return false;
}
status = ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_MODE_ASYNCHRONOUS |
data_bits |
parity |
stop_bits |
ARM_USART_FLOW_CONTROL_NONE,
line_coding - > dwDTERate);
if (status != ARM_DRIVER_OK) {
return false;
}
// Store requested settings to local variable
cdc_acm_line_coding = * line_coding;
uart_rx_cnt = 0;
usb_tx_cnt = 0;
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_CONTROL_TX, 1 U);
ptrUART - > Control(ARM_USART_CONTROL_RX, 1 U);
ptrUART - > Receive(uart_rx_buf, UART_BUFFER_SIZE);
return true;
}
// Called upon USB Host request to retrieve communication settings.
// \param[out] line_coding pointer to CDC_LINE_CODING structure.
// \return true get line coding request processed.
// \return false get line coding request not supported or not processed.
bool USBD_CDC0_ACM_GetLineCoding(CDC_LINE_CODING * line_coding) {
// Load settings from ones stored on USBD_CDC0_ACM_SetLineCoding callback
* line_coding = cdc_acm_line_coding;
return true;
}
// Called upon USB Host request to set control line states.
// \param [in] state control line settings bitmap.
// - bit 0: DTR state
// - bit 1: RTS state
// \return true set control line state request processed.
// \return false set control line state request not supported or not processed.
bool USBD_CDC0_ACM_SetControlLineState(uint16_t state) {
// Add code for set control line state
(void)(state);
return true;
}
//! [code_USBD_User_CDC_ACM]
[/code]
Is it possible to run the lpc1768 as a USB listener and also perform a set of tasks in parallel? If yes, how should I go about it?
Hello Kevin,
What do you mean about a USB listener? Do you plan to use one of the USB instances as host and the other as a device and process the packages in the middle of a USB communication?
I think this will be a little difficult to do this with this MCU. The speed to receive the messages and interchanging it between them with the frequency used by the USB will be a little difficult with the core frequency and will not leave much time for other tasks.
Best Regards,
Alexis Andalon
Hi,
>What do you mean about a USB listener? Do you plan to use one of the USB instances as host and the other as a device and process the >packages in the middle of a USB communication?
No, it's a direct link between a master and a slave that talk through a VirtualCOM port over USB.
Thx!
Kevin
Hello Kevin,
This MCU has a ROM library that implements some of the functions so you only need to fill the structures and the ROM code will do all the work.
Since you don't have two cores in this MCU you can't run the task in parallel but you could use some kind of synchronization or an RTOS (there's a FreeRTOS example in the LPCOpen).
Best Regards,
Alexis Andalon
Hi,
I've managed to get it to run but have another problem with keil's component manager and made a post but it's currently pending.
Best,
Kev