- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- Wireless ConnectivityWireless Connectivity
- RFID / NFCRFID / NFC
- Advanced AnalogAdvanced Analog
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
- S32Z/E
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- Generative AI & LLMs
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
- RFID / NFC
- Advanced Analog
-
- NXP Tech Blogs
- Home
- :
- General Purpose Microcontrollers
- :
- LPC Microcontrollers
- :
- Using Keil to load binary into external SPI Flash
Using Keil to load binary into external SPI Flash
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Using Keil to load binary into external SPI Flash
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
I'm wondering if there's a way to load a random binary file into external SPI flash using Keil. The binary file will pass through the LPC54102 (OM13077 EVK board). I know some ISEs for FPGAs allow you to do this, curious if this is possible with the LPC54102 using Keil.
Obviously Keil will need to know what SPI flash is connected to the LPC, along with other details like, SPI port, clk speed, etc.
Does anyone know is Keil can do this?

- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello @rhsalced
- You can refer to this thread:
It introduces lpc54018 + QSPI flash + KEIL.。
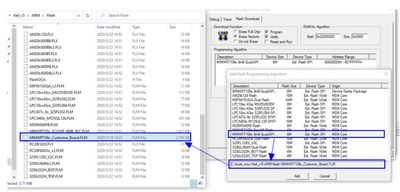
- 1. If the default selected Flash download algorithm file is not applicable to your board, then you need to provide a suitable algorithm file (.FLM) yourself and place it in the MDK installation directory (\Keil_v5\ARM\Flash). Then, reopen the project options, and the newly added algorithm will be automatically refreshed into the list of selectable algorithms.

The Flash download algorithm under Keil MDK is open-source and comes with relatively detailed documentation. The documentation can be found on the GitHub homepage of arm-software. Based on these documents, we can basically understand the design details of its download algorithm.
Algorithm Homepage:
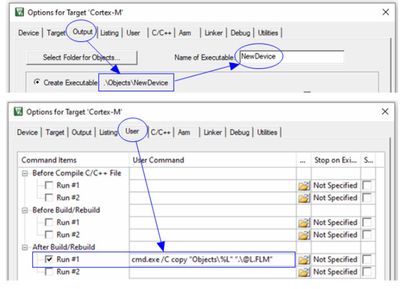
3.1 Download Algorithm Template Project
Keil MDK provides a basic template project for the Flash download algorithm. The project is located at \Keil_v5\ARM\Flash_Template\NewDevice.uvprojx. This project can only be compiled using MDK (not supported by MDK-Lite). In addition to the project settings, this template project only contains four files:
\Keil_v5\ARM\Flash\FlashOS.h
\Keil_v5\ARM\Flash_Template\FlashDev.c
\Keil_v5\ARM\Flash_Template\FlashPrg.c
\Keil_v5\ARM\Flash_Template\Target.lin
After obtaining the basic template project, we need to change the default ARMCM0 core in the project options according to the type of the target MCU core. Then, we need to implement all the algorithm API functions in FlashDev.c and FlashPrg.c (they are empty by default). Finally, compile the project to generate the.FLM file, which is the algorithm file we need (in fact, the final.FLM file is obtained by directly renaming the.axf file through the script command in After Build. The.FLM file is essentially an axf format file).
The structure of the algorithm itself is actually very simple. In the FlashDev.c file, there is a constant structure named FlashDevice, and its prototype is defined in FlashOS.h. This structure mainly provides the necessary Flash information for the IDE, and its values must be filled in correctly according to the actual situation of the board.
struct FlashDevice const FlashDevice = {
FLASH_DRV_VERS, // Driver Version, do not modify!
"New Device 256kB Flash", // Device Name
ONCHIP, // Device Type
0x00000000, // Device Start Address
0x00040000, // Device Size in Bytes (256kB)
1024, // Programming Page Size
0, // Reserved, must be 0
0xFF, // Initial Content of Erased Memory
100, // Program Page Timeout 100 mSec
3000, // Erase Sector Timeout 3000 mSec
// Specify Size and Address of Sectors
0x002000, 0x000000, // Sector Size 8kB (8 Sectors)
0x010000, 0x010000, // Sector Size 64kB (2 Sectors)
0x002000, 0x030000, // Sector Size 8kB (8 Sectors)
SECTOR_END
};