- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- Wireless ConnectivityWireless Connectivity
- RFID / NFCRFID / NFC
- Advanced AnalogAdvanced Analog
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
- S32Z/E
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- Generative AI & LLMs
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
- RFID / NFC
- Advanced Analog
-
- NXP Tech Blogs
- Home
- :
- General Purpose Microcontrollers
- :
- Kinetis Microcontrollers
- :
- Re: flash operations
flash operations
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
flash operations
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Why does the PFlash SDK example take more time to write to flash compared to the bootloader, even though both use the same functions for writing to flash?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello @RajPadmani ,
Thanks for your post. To better support you, could you please provide me with more details? Specifically, I'd like to know the model of the MCU you are using, the IDE you've chosen, the version of the SDK, and the type of the bootloader.
Have a good day,
Celeste
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello @RajPadmani ,
I couldn't find the bootloader example in the KM34 SDK.
Could you describe the problem in more detail? Also, how did you conduct the tests? Based on the current information you've provided, we're unable to pinpoint the problem.
BRs,
Celeste
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
There is no SDK example for the MKM34Z256VLQ7 bootloader, so I customized the MKM35 bootloader to run on the MKM34, and it worked perfectly.
In the bootloader, I read the application and write it using the "mem_write" function, which writes one sector significantly faster compared to the "flash_program" function from the "PFlash" SDK example for the MKM34Z256VLQ7.
Even after matching the clock speed with the bootloader code, the "PFlash" SDK example still takes longer for writing and erasing.
What could be the reason for this difference in performance?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
To clarify the differences between the "mem_write" function and the "flash_program" function, I need to understand their specific implementation methods. Given that you are using a customized bootloader, I'm not sure how "mem_write" is implemented, and I haven't been able to find relevant content in the API Reference Manual either.
I wonder if you could send me this part of the code. If you have referred to any existing SDK projects or ANs, please let me know as well.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I am using this bootloader in the KM34 microcontroller. In the bootloader code, I only changed the memory addresses to make it compatible with the KM34.
The mem_write function is a wrapper that uses the flash_program function to write to flash. However, it executes faster than the flash_program function, which I used directly in my application.
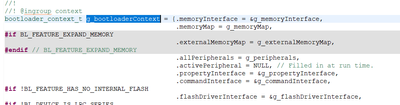
You can find this function in "bl_context.c"
In this file, there is a structure named g_bootloaderContext, which contains a structure variable called memoryInterface. The value of g_memoryInterface is assigned to it, and within g_memoryInterface, you will find the mem_write function.
I have attached the bootloader SDK example that I'm using.