- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- Wireless ConnectivityWireless Connectivity
- RFID / NFCRFID / NFC
- Advanced AnalogAdvanced Analog
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
- S32Z/E
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- Generative AI & LLMs
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
- RFID / NFC
- Advanced Analog
-
- NXP Tech Blogs
- Home
- :
- 製品フォーラム
- :
- デジタルシグナルコントローラ
- :
- What is the function of the Per_Toff parameter in the motor control library?
What is the function of the Per_Toff parameter in the motor control library?
- RSS フィードを購読する
- トピックを新着としてマーク
- トピックを既読としてマーク
- このトピックを現在のユーザーにフロートします
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- 印刷用ページ
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
When I was looking at the document AN1913 3-phase BLDC Motor Control with Sensorless Back-EMF ADC Zero Crossing Detection using 56F80x.pdf, there was a description of Per_Toff, but it confused me.
1、
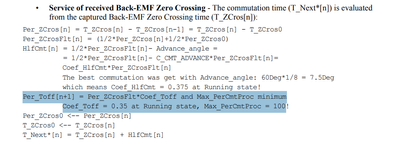
From the description in the screenshot above, during the Per_Toff time, it is in an unstable state of Zero Crossing, and therefore detection cannot be performed.
2、
From the description in the screenshot above, it seems that Zero Cross detection is required during the Per_Toff time.
Can there be a more explicit and detailed explanation of this parameter?
thanks.
解決済! 解決策の投稿を見る。
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
Hello @TQF ,
Thanks for your post. Here are the two points that you think are contradictory. Let me explain them.
1、 From the description in the screenshot above, during the Per_Toff time, it is in an unstable state of Zero Crossing, and therefore detection cannot be performed.
[A] Your understanding is correct. During the Per_Toff time after commutation, the main purpose is to stabilize the back electromotive force waveform. At this time, zero-crossing detection is indeed not carried out because the signal is unstable and prone to misjudgment.
2、From the description in the screenshot above, it seems that Zero Cross detection is required during the Per_Toff time.
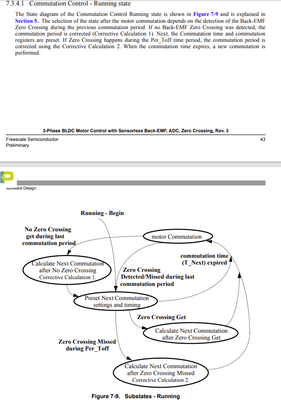
[A] There is a deviation in the understanding of this point. Judging from Figure 5-7, Figure 5-8 and the description in 7.3.4.1, zero-crossing detection is not carried out within the Per_Toff time. In these contents, zero-crossing detection is an event of concern throughout the commutation cycle, while the Per_Toff time is the stage used to stabilize the back electromotive force waveform after the commutation is completed. When the zero-crossing is detected before the preset commutation time, the commutation time will be adjusted according to the zero-crossing time; if the zero-crossing is not detected within the preset commutation cycle, corresponding correction calculations will also be carried out, instead of performing zero-crossing detection within the Per_Toff time.
1) Suppressing interference and stabilizing the back electromotive force waveform: When the motor is running, after the commutation operation, due to the influence of electromagnetic interference and the reverse current in the freewheeling diode, spikes will be generated on the back electromotive force signal. These spikes may lead to misjudgment in the zero-crossing detection of the back electromotive force. Setting the Per_Toff time is to make the waveform of the back electromotive force stable during this period, avoiding zero-crossing detection errors caused by interference.
2) A key basis for determining the commutation time: In the calculation process of the commutation time, Per_Toff is an important parameter. According to the calculation formula in the document, for example, in the running state, Per_Toff[n + 1] = Per_ZCrosFlt * Coef_Toff (where Coef_Toff = 0.35).
When the zero-crossing of the back electromotive force is detected, the new commutation time will be calculated according to the relevant formula, and Per_Toff is involved in this calculation process, affecting the determination of the commutation time. The description of the commutation time calculation in Section 5.4.2.2 reflects the role of Per_Toff in the commutation time calculation.
3) Coordinating zero-crossing detection and commutation operation: In the software control logic, the Per_Toff time is closely related to the zero-crossing detection. In the running state, if the zero-crossing of the back electromotive force is not detected within the preset commutation cycle (Per_CmtPreset[n]), relevant correction calculations will be carried out; if the zero-crossing is detected within the Per_Toff time, the commutation time will be corrected in another way. This shows that the Per_Toff time is involved in the coordination of the zero-crossing detection and the commutation operation, ensuring the accurate and stable operation of the motor. The state diagrams and descriptions in Figure 5-7 and Section 7.3.4.1 show this coordination relationship.
Hope it can help you.
BRs,
Celeste
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: If this post answers your question, please click the "ACCEPT AS SOLUTION" button. Thank you!
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
Hello @TQF ,
Thanks for your post. Here are the two points that you think are contradictory. Let me explain them.
1、 From the description in the screenshot above, during the Per_Toff time, it is in an unstable state of Zero Crossing, and therefore detection cannot be performed.
[A] Your understanding is correct. During the Per_Toff time after commutation, the main purpose is to stabilize the back electromotive force waveform. At this time, zero-crossing detection is indeed not carried out because the signal is unstable and prone to misjudgment.
2、From the description in the screenshot above, it seems that Zero Cross detection is required during the Per_Toff time.
[A] There is a deviation in the understanding of this point. Judging from Figure 5-7, Figure 5-8 and the description in 7.3.4.1, zero-crossing detection is not carried out within the Per_Toff time. In these contents, zero-crossing detection is an event of concern throughout the commutation cycle, while the Per_Toff time is the stage used to stabilize the back electromotive force waveform after the commutation is completed. When the zero-crossing is detected before the preset commutation time, the commutation time will be adjusted according to the zero-crossing time; if the zero-crossing is not detected within the preset commutation cycle, corresponding correction calculations will also be carried out, instead of performing zero-crossing detection within the Per_Toff time.
1) Suppressing interference and stabilizing the back electromotive force waveform: When the motor is running, after the commutation operation, due to the influence of electromagnetic interference and the reverse current in the freewheeling diode, spikes will be generated on the back electromotive force signal. These spikes may lead to misjudgment in the zero-crossing detection of the back electromotive force. Setting the Per_Toff time is to make the waveform of the back electromotive force stable during this period, avoiding zero-crossing detection errors caused by interference.
2) A key basis for determining the commutation time: In the calculation process of the commutation time, Per_Toff is an important parameter. According to the calculation formula in the document, for example, in the running state, Per_Toff[n + 1] = Per_ZCrosFlt * Coef_Toff (where Coef_Toff = 0.35).
When the zero-crossing of the back electromotive force is detected, the new commutation time will be calculated according to the relevant formula, and Per_Toff is involved in this calculation process, affecting the determination of the commutation time. The description of the commutation time calculation in Section 5.4.2.2 reflects the role of Per_Toff in the commutation time calculation.
3) Coordinating zero-crossing detection and commutation operation: In the software control logic, the Per_Toff time is closely related to the zero-crossing detection. In the running state, if the zero-crossing of the back electromotive force is not detected within the preset commutation cycle (Per_CmtPreset[n]), relevant correction calculations will be carried out; if the zero-crossing is detected within the Per_Toff time, the commutation time will be corrected in another way. This shows that the Per_Toff time is involved in the coordination of the zero-crossing detection and the commutation operation, ensuring the accurate and stable operation of the motor. The state diagrams and descriptions in Figure 5-7 and Section 7.3.4.1 show this coordination relationship.
Hope it can help you.
BRs,
Celeste
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: If this post answers your question, please click the "ACCEPT AS SOLUTION" button. Thank you!
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------