- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- Wireless ConnectivityWireless Connectivity
- RFID / NFCRFID / NFC
- Advanced AnalogAdvanced Analog
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
- S32Z/E
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- Generative AI & LLMs
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
- RFID / NFC
- Advanced Analog
-
- NXP Tech Blogs
- Home
- :
- General Purpose Microcontrollers
- :
- Kinetis Microcontrollers
- :
- SPI Flash: Using external Flash as program memory
SPI Flash: Using external Flash as program memory
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
SPI Flash: Using external Flash as program memory
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I had used mostly internal Flash memory (up to 1MB) in Kinetis K22 / K24 / K26.
But with the popularity of Quad SPI Flash support within the Kinetis microcontroller line, I have the following questions:
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using external Flash for program memory? Ex. price point, hardware integration, expansion, code security, ease of programming into Flash.
2. Are there any benchmark on performance of external vs internal Flash?
3. How can we make it easy to program external Flash program in high volume production?
4. How do we secure the firmware code within these external Flash memory? ex. to prevent unauthorized reading of code, etc.
Thanks in advance.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Jonathan,
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using external Flash for program memory?
advantage: Compare with FMC/FSMC, QSPI support low cost and small package NOR flash. It use less IO pad, decrease PCB size effectively, and decrease the design complexity of PCB. Compare to internal Flash, QSPI well extend the memory size with very low cost.
disadvantage: Run on QSPI is slow than internal flash when MCU use high clock speed. Debug on QSPI is also a bit complex.
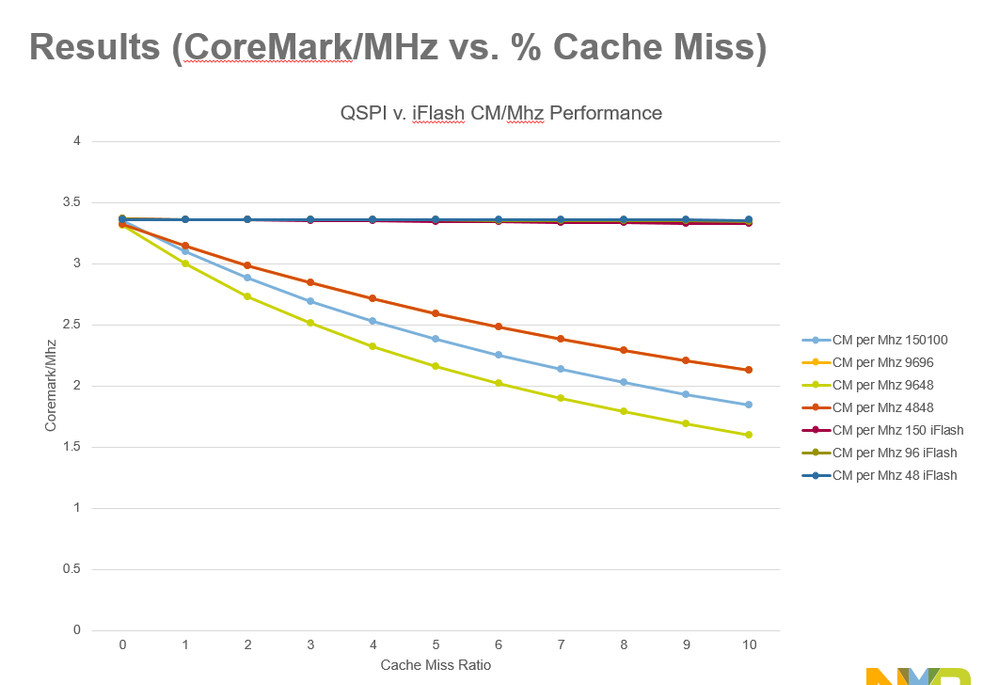
2. Are there any benchmark on performance of external vs internal Flash?
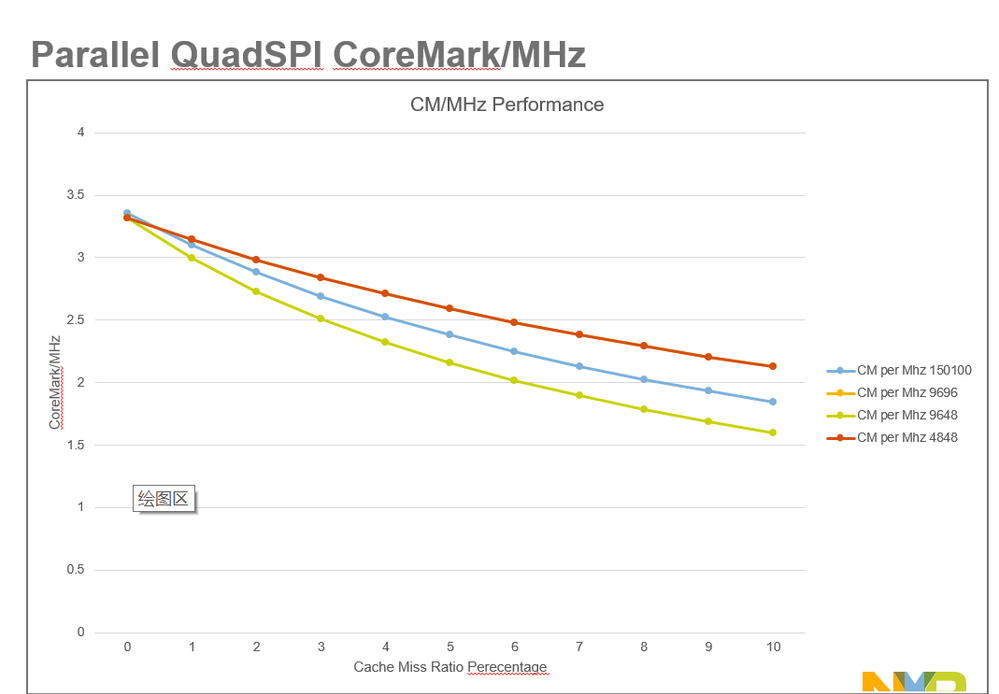
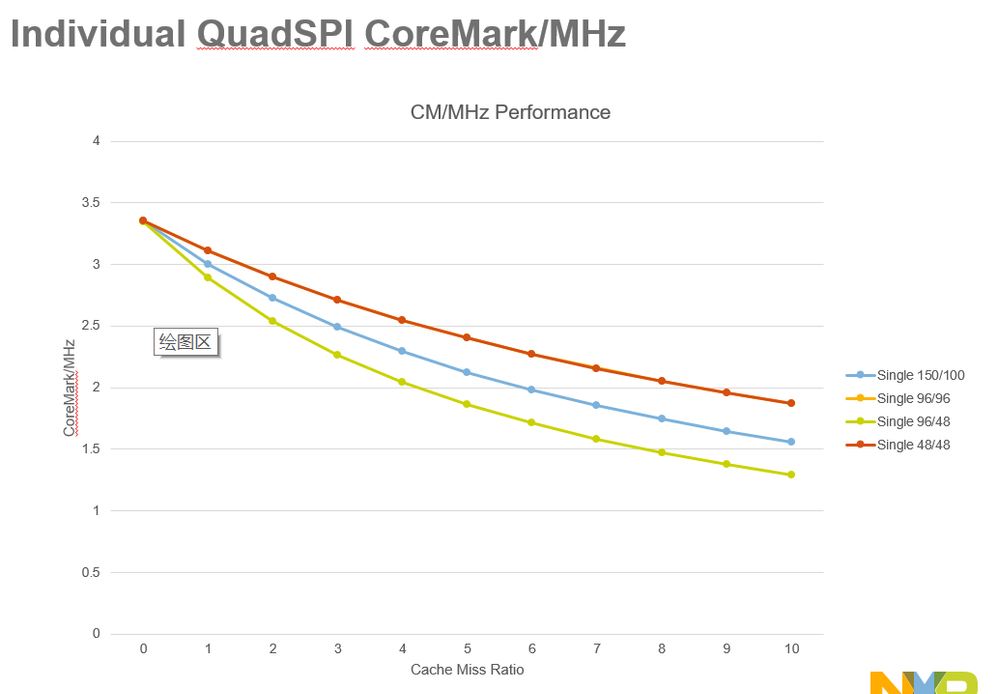
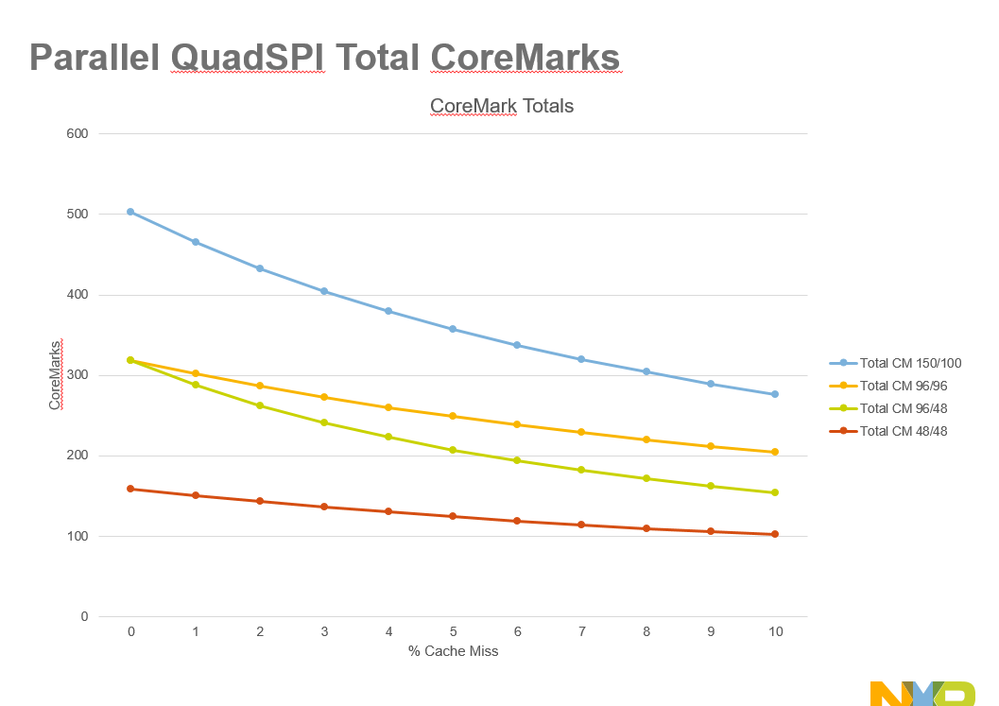
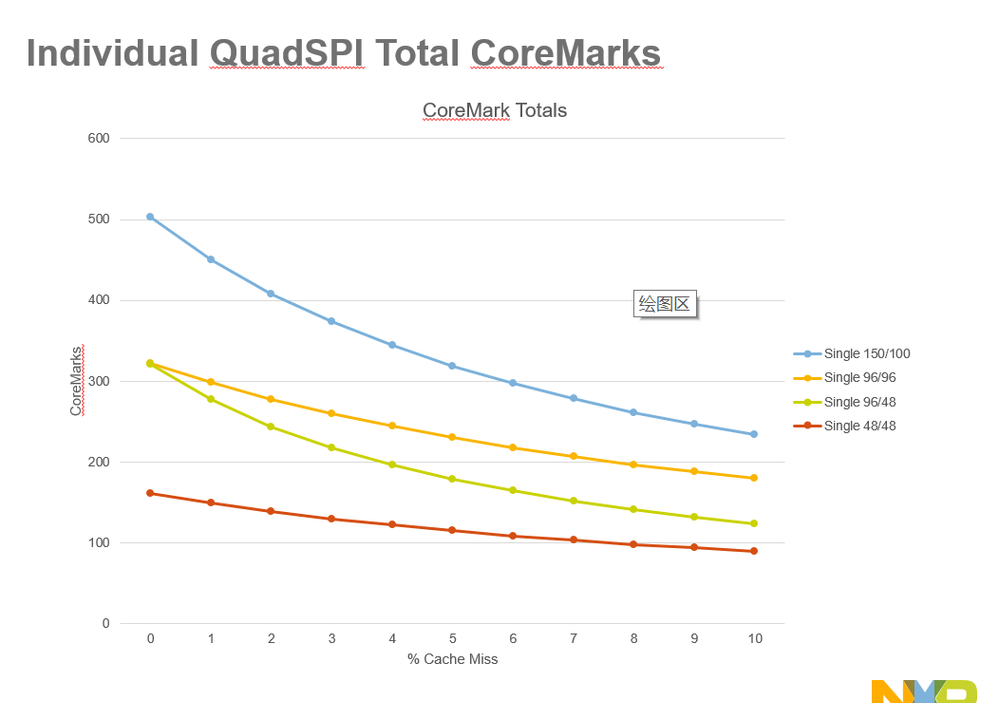
Modified CoreMark benchmark application (added code for cache manipulation and execution time capture)
Force 1%, 2%, 3%....10% cache misses by doing X number of iterations and executing n% with cache disabled and (100-n)% with code cache enabled. X = 4000 for these results.
Cache miss vs. Cache off performance is not equal. Cache miss adds delay cycle for search and replace.
QuadSPI Configuration
- System at 1.8V Core VDD and IO VDD
- IRC48 and 32kHz clock
- Alias code region
- Parallel (8-bit) and Individual (4-bit)
- SDR, 100, 96, and 48 MHz
- Sys Cache on/off
- Data mapped to internal > 0x2000_0000 memory space
- 512-byte Flexible AHB buffer
3. How can we make it easy to program external Flash program in high volume production.
NXP has tools for that. Blhost is used in command line and KinetisFlashTools The Kinetis Flash Tool is a GUI application on Windows® OS, aiming to offer the user an ease-of-use friendly user interface to communicate with the Kinetis device, running the Kinetis bootloader application.
4. How do we secure the firmware code within these external Flash memory?
When generate .SB file, you can use a key file to encrypt content. So the content in SPI flash is ciphertext.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks Jing for the detailed responses. You are such a great help to me.
Here are some questions: Feel free to answer estimates or typical values below.
1-2) Are my estimates below pretty close (typical) for QSPI vs Internal Flash benchmark speeds? I've used Cypress FL064L as reference.
QSPI Internal flash
read: 6-52MB/s , 40-250MB/s
write: 569KB/s , 200kB/s
3) Good
4) Does this meant all SPI transactions will be encrypted? Will this add more delay time (the encryption/decryption)?
Regards,
Jonathan
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Jing,
Thanks for detailed response. You are such a great help to me.
1-2) Do you think my estimates below are pretty typical (ballpark)? For QSPI Flash, I've used Cypress FL064L as reference.
QSPI Internal flash
read: 6-52MB/s , 40-250MB/s
write: 569KB/s , 200kB/s
3) Good
4) Will .SB decryption will almost be real-time (or doesn't add delay time)? Does this meant all transaction on SPI line will be encrypted? Is the program being run inside the Flash memory?