- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- Wireless Connectivity
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- MCUXpresso Training Hub
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
-
- Home
- :
- i.MXプロセッサ
- :
- i.MXプロセッサ ナレッジベース
- :
- The usage of SAI on i.MX6UL & i.MX7D/S for Hardware design
The usage of SAI on i.MX6UL & i.MX7D/S for Hardware design
- RSS フィードを購読する
- 新着としてマーク
- 既読としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- 印刷用ページ
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
The usage of SAI on i.MX6UL & i.MX7D/S for Hardware design
The usage of SAI on i.MX6UL & i.MX7D/S for Hardware design
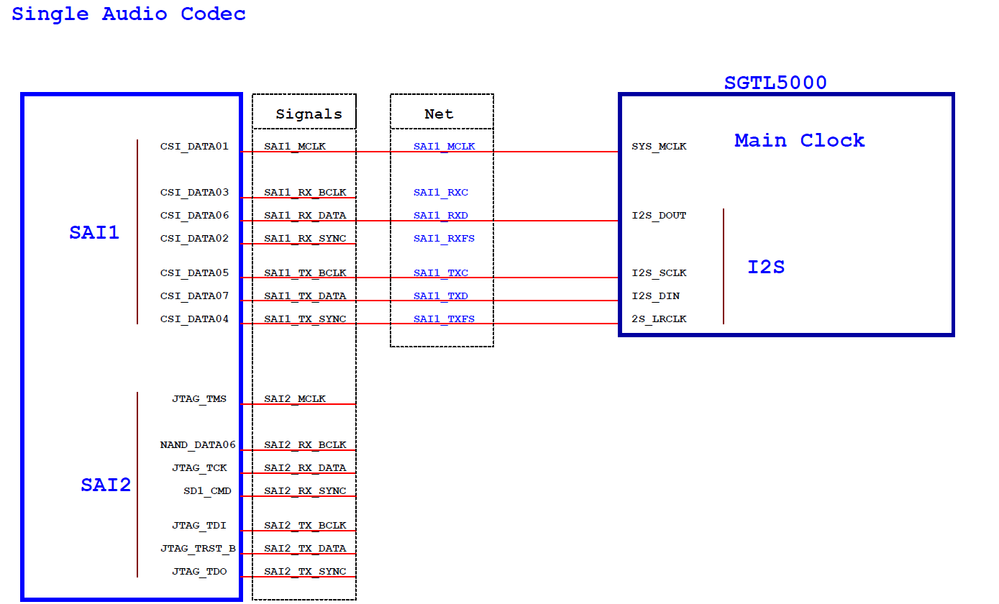
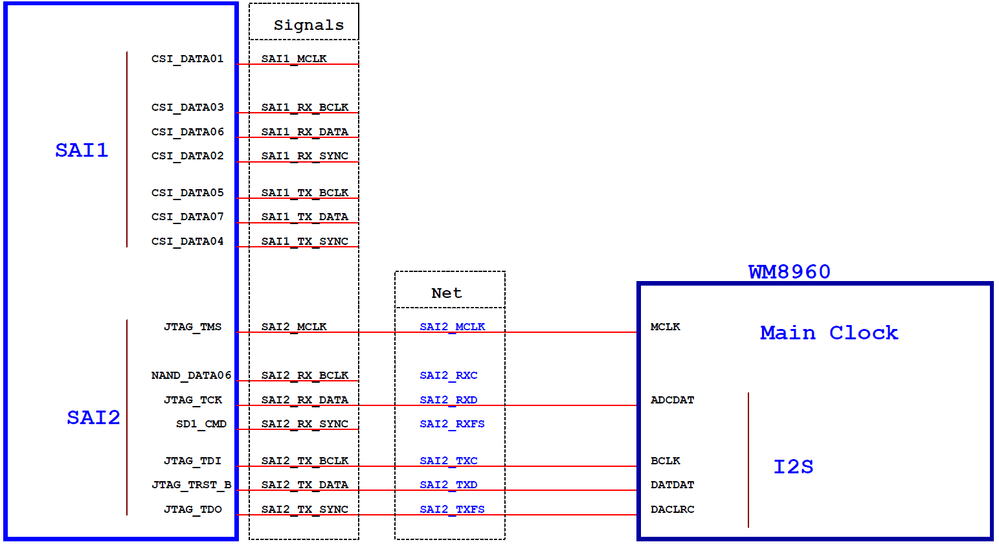
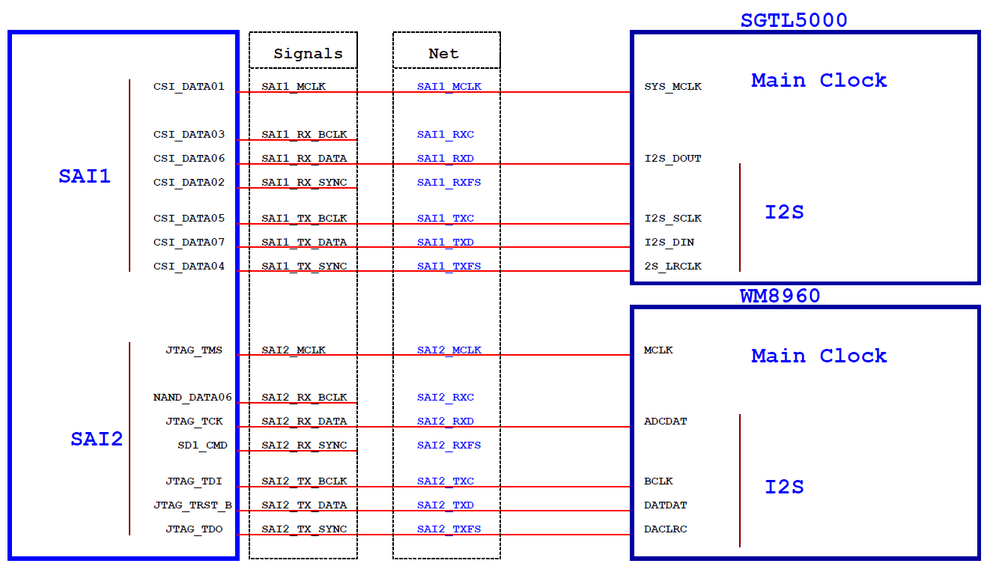
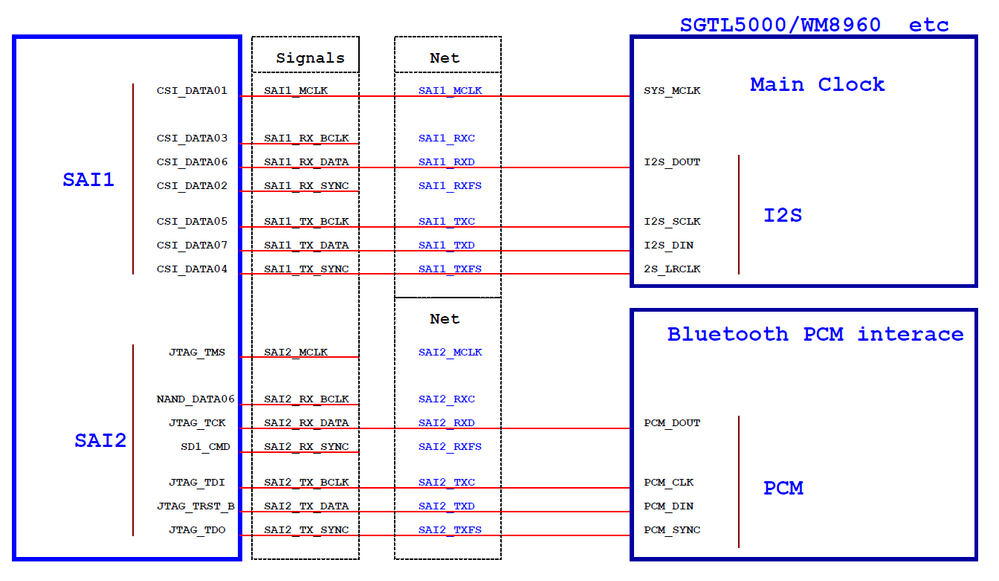
Of all the i.MX serials SoC, i.MX28/i.MX6UL/i.MX7D/S use Synchronous Audio Interface(SAI) to support audio applications. SAI supports I2S, AC97, TDM and code/DSP interfaces. The SAI interface consists of these signals:
SAI_MCLK ------------ used to provide working clock for external audio device , such as audio codec.
SAI_RX_BCLK ------------ bit clock for receiving channle.
SAI_RX_DATA ------------ data of receiving channel.
SAI_RX_SYNC ------------ Frame Synchronous signal of Left and right channel for receiving channel.
SAI_TX_BCLK ------------ bit clock for transmitting channel.
SAI_TX_DATA ------------ data of transmitting channel
SAI_TX_SYNC ------------ Frame Synchronous signal of Left and right channel for transmitting channel.
According to above signals, SAI has 2 channels: receive and transmit, and these 2 channels have their own clock: bit clock and frame SYNC, so they can work independently, it means PLAY and CAPTURE can be operated simultaneously, that is to say, SAI works at Asynchronous mode this moment.
In the document, we will discuss several usages of SAI on hardware design when it works at I2S(SYNC) mode. we will take i.MX6UL as an example, and for i.MX7D/S, usages are similar.
1. IOMUX of SAI
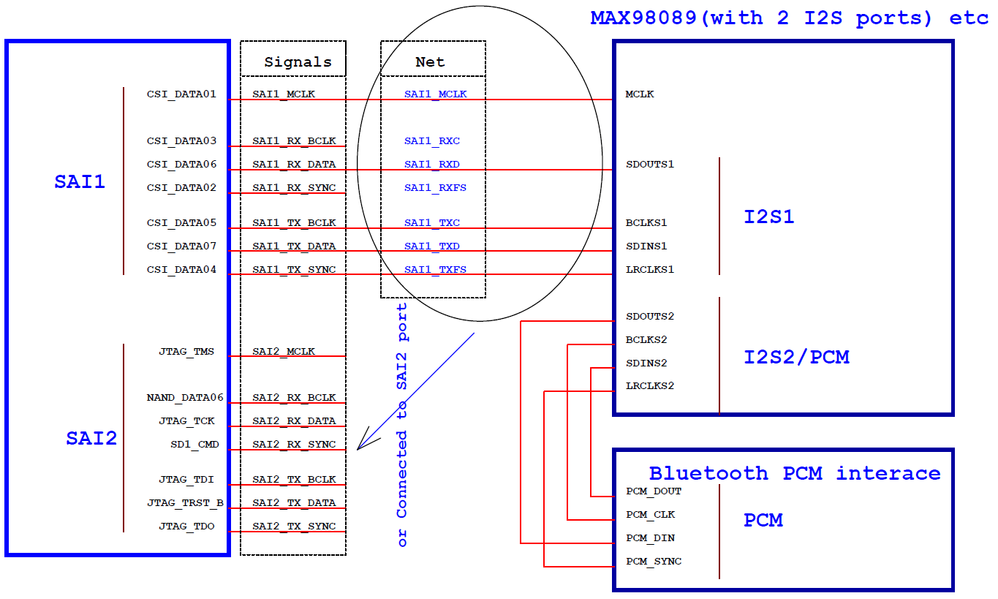
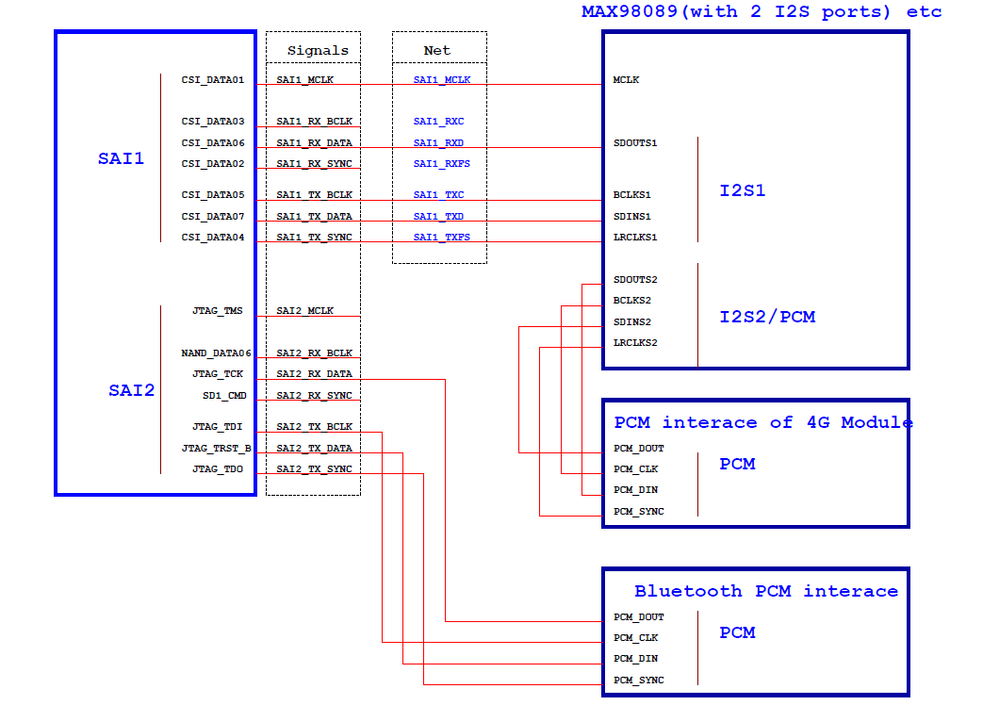
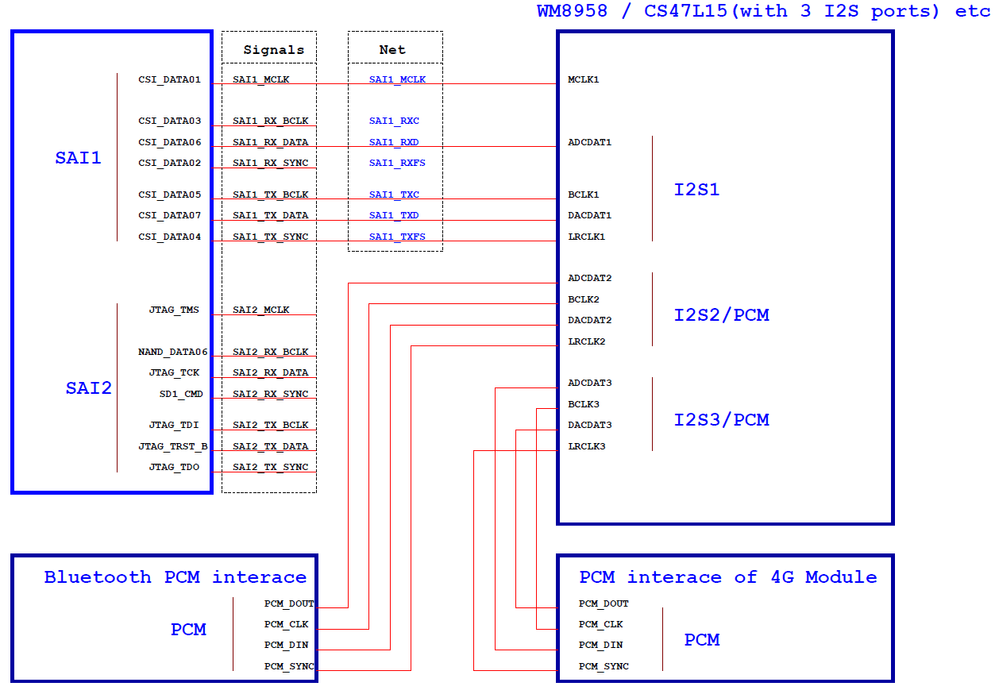
From i.MX6UL reference manual, there are 3 SAI modules in i.MX6UL: SAI1 , SAI2 & SAI3, see page 2529 in IMX6ULRM.pdf. As common applications, we will use 2 interface of SAIs.
2. Hardware connections for I2S mode
Either CPU is Master or Codec is Master, hardware connections are same.
(1) Single audio codec
or
(2) Dual audio codec
(3) Audio codec + Bluetooth PCM
or
(4) Audio codec + Bluetooth PCM + 4G PCM
or
[Note] Attachments are schematics of WM8958 and MAX98089, which are not released by NXP, just for users who are interested in i.MX audio applications reference. If you want to use WM98089 or WM8958, please contact their manufactures and confirm if schematics are correct, so don't use them directly for your solution.
NXP China
TIC i.MX team
Weidong Sun