- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- Wireless Connectivity
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- MCUXpresso Training Hub
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
-
- Home
- :
- ソフトウェア・フォーラム
- :
- S32 SDK
- :
- Linker script section alignment exceeds memory region size (RTD, AR: 4.7.0, SW: 2.0.0)
Linker script section alignment exceeds memory region size (RTD, AR: 4.7.0, SW: 2.0.0)
- RSS フィードを購読する
- トピックを新着としてマーク
- トピックを既読としてマーク
- このトピックを現在のユーザーにフロートします
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- 印刷用ページ
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
Hello,
I have installed the S32DS v3.5.12 together with the latest RTD (AR: 4.7.0, SW: 2.0.0) for an S32k148 MCU.
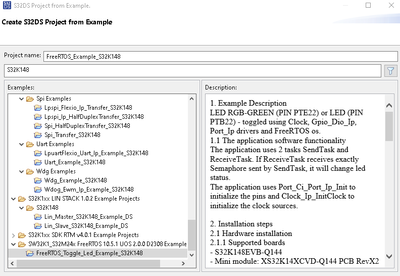
I have generated the FreeRTOS example project for the S32K148 MCU as shown in the image below.
I have studied the Linker file linker_flash_s32k148.ld and think I found an error in the generated file. First, examine the memory definition. According to the file 1024 bytes are reserved for the interrupt table inside the flash memory and then additional 16 bytes for the flash configuration flags/bits, etc.
MEMORY
{
int_flash_interrupts : ORIGIN = 0x00000000, LENGTH = 0x00000400 /* 1K */ /* Do not change this section */
int_flash_config : ORIGIN = 0x00000400, LENGTH = 0x00000010 /* 16bytes */ /* Do not change this section */
int_flash : ORIGIN = 0x00000410, LENGTH = 0x0017FBF0 /* ~1.5MB */
int_sram_results : ORIGIN = 0x1FFE0000, LENGTH = 0x00000100 /* 256bytes */
int_sram : ORIGIN = 0x1FFE0100, LENGTH = 0x0003DF00 /* ~248K */
int_sram_stack_c0 : ORIGIN = 0x2001E000, LENGTH = 0x00001000 /* 4K */
ram_rsvd2 : ORIGIN = 0x2001F000, LENGTH = 0 /* End of SRAM */
}If you continue analyzing the section definition at the beginning
SECTIONS
{
.flash_interrupts :
{
. = ALIGN(2048);
__interrupts_rom_start = .;
KEEP(*(.intc_vector))
. = ALIGN(4);
__interrupts_rom_end = .;
} > int_flash_interrupts
you see that the memory region int_flash_interrupts, which has an assigned size of 1024 bytes contains a 2048 byte alignment instruction, which exceeds the defined region size.
Am I correct? If not, can you explain, what I am missing here.
Best regards,
M_SCH
解決済! 解決策の投稿を見る。
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
Hi @M_SCH
The ALIGN(n) instructs the compiler to align a variable on an n-byte boundary starting from the ORIGIN address. This just limits the location of a memory region to a certain n-byte size, this should not interfere with other memory regions as the memory region size does not exceed the n-byte boundary.
B.R.
VaneB
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
Hi @M_SCH
The ALIGN(n) instructs the compiler to align a variable on an n-byte boundary starting from the ORIGIN address. This just limits the location of a memory region to a certain n-byte size, this should not interfere with other memory regions as the memory region size does not exceed the n-byte boundary.
B.R.
VaneB