- NXP Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- Wireless Connectivity
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- Vigiles
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- RSS フィードを購読する
- トピックを新着としてマーク
- トピックを既読としてマーク
- このトピックを現在のユーザーにフロートします
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- 印刷用ページ
LPSPI interfacing flash using S32K312 RTD
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
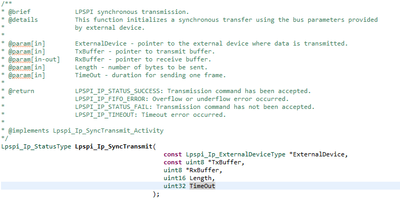
Hello i am using S32K312, i need to interface the Spansion S25 flash using RTD, i am using Lpspi_Ip_SyncTransmit() function to transmit and receive the data , but the function description tells the length parameter is number of bytes to send, but how can we receive the required number of bytes using the same function?
i
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
Hello @VaneB,
Can you please tell me how the LPSPI functions work if we have different transmit and receive bytes?
For instance i need to send X bytes and need receive Y bytes( in my case with SPI flash i need to send 4 byte data(command+address) and need to receive the required number of bytes) with LPSPI functions.
Please let me know.
Sincerly,
Sai Praveen Bodhanapu.
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
I suggest you test the LPSPI examples included in the RTD. To know how the module works.
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
If you take a look at the Lpspi_Ip_SyncTransmit(), this function calls Lpspi_TransmitTxInit() and Lpspi_TransmitRxInit() which receives as a parameter their respective buffer and the same length which is the one defined in the call of Lpspi_Ip_SyncTransmit().
This means that this function was designed so that transmission and reception work with the same number of bytes.
Please let me know if the explanation is clear or if it is not what you were looking for.
B.R.
VaneB
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
- 新着としてマーク
- ブックマーク
- 購読
- ミュート
- RSS フィードを購読する
- ハイライト
- 印刷
- 不適切なコンテンツを報告
Synchronous communication is a method in which a continuous stream of data signals is accompanied by a clock signal to ensure that the transmitter and receiver are synchronized with each other.
Asynchronous communication, on the other hand, did not require a clock signal since the data is synchronized through signals, which indicate the start of the new byte or message.