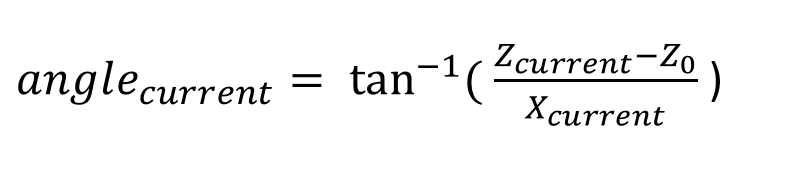- Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- Wireless ConnectivityWireless Connectivity
- RFID / NFCRFID / NFC
- Advanced AnalogAdvanced Analog
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
- S32M
- S32Z/E
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
- Generative AI & LLMs
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
- Cloud Lab Forums
-
- Knowledge Bases
- ARM Microcontrollers
- i.MX Processors
- Identification and Security
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- QorIQ Processing Platforms
- S32 Automotive Processing Platform
- Wireless Connectivity
- CodeWarrior
- MCUXpresso Suite of Software and Tools
- MQX Software Solutions
- RFID / NFC
- Advanced Analog
-
- NXP Tech Blogs
How to detect the Direction and Angle using XZ-accelerometer Sensor
Dear All,
I am using FXTH8719xxxx Family XZ axis Accelerometer Sensor. I need to find the direction as well how much angle turned by using X-axis ans Z Axis data. If any one can help me the possibility?
Each sensor Z-Axis have the different offset values, help me how to calibrate the Z-axis with the new sensor.
hi Anthony,
I have one points to clarify,
what is the values for Z0 - Z base values, How to find the Z base values?
Thanks,
Sakthivel K
Dear Anthony,
Thanks for your response. Your points are very helpful i'm collecting z-x axis data so i will apply your method if any points to clarify i get back to you.
Regards,
Sakthivel K
Hi Hulandaivel,
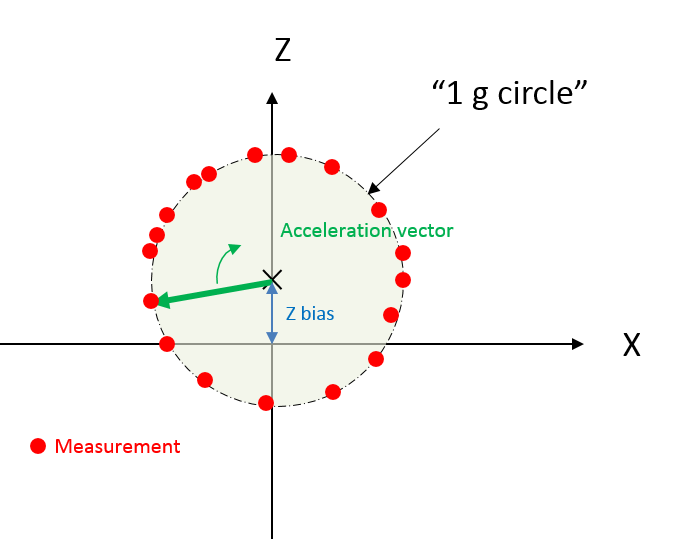
There are several methods to calibrate sensor offsets. The big limitation with an accelerometer is you need to do the calibration phase with quasi-static data. I mean: if you move the FXTH8719xxxx , you will add an acceleration vector on both axis (Z & X) and this will degrade/pervert the calibration... So you have to take care of the sensor rotation by doing very smooth motion (external acceleration should be very small compared to the 1g-force).
About calibration algorithms:
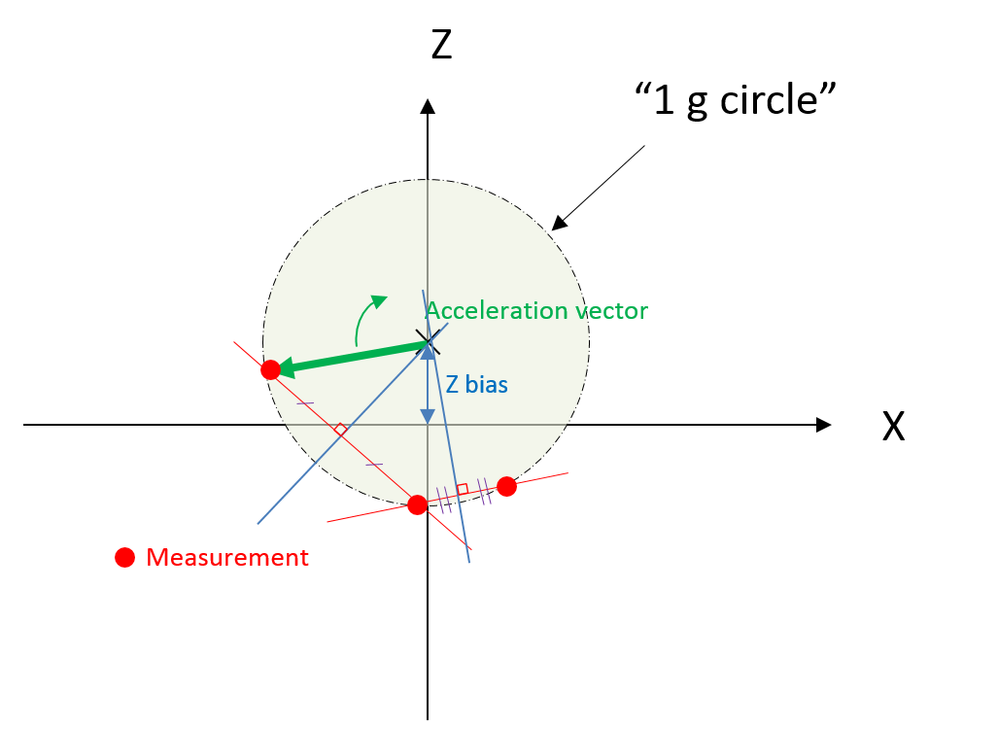
1. You can collect data/measurements around the circle in a buffer. When the full revolution is done, you compute the Z offset with an optimization method to minimize the standard deviation of the 1g vector on all measurements.
2. You can calculate the circle center with 3 points only. (Basic equations & resolution)
------
The final angle can be calulated with the following equation:
-Z0 the Z bias
- Z current / X current are the actual measurements.
Note that these equations are only valid in a static model and are using the 1g gravitational force as reference.
I hope it helps.
Thanks,
Anthony