- NXP Forums
- Product Forums
- General Purpose MicrocontrollersGeneral Purpose Microcontrollers
- i.MX Forumsi.MX Forums
- QorIQ Processing PlatformsQorIQ Processing Platforms
- Identification and SecurityIdentification and Security
- Power ManagementPower Management
- MCX Microcontrollers
- S32G
- S32K
- S32V
- MPC5xxx
- Other NXP Products
- Wireless Connectivity
- S12 / MagniV Microcontrollers
- Powertrain and Electrification Analog Drivers
- Sensors
- Vybrid Processors
- Digital Signal Controllers
- 8-bit Microcontrollers
- ColdFire/68K Microcontrollers and Processors
- PowerQUICC Processors
- OSBDM and TBDML
-
- Solution Forums
- Software Forums
- MCUXpresso Software and ToolsMCUXpresso Software and Tools
- CodeWarriorCodeWarrior
- MQX Software SolutionsMQX Software Solutions
- Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)Model-Based Design Toolbox (MBDT)
- FreeMASTER
- eIQ Machine Learning Software
- Embedded Software and Tools Clinic
- S32 SDK
- S32 Design Studio
- Vigiles
- GUI Guider
- Zephyr Project
- Voice Technology
- Application Software Packs
- Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK)
- Processor Expert Software
-
- Topics
- Mobile Robotics - Drones and RoversMobile Robotics - Drones and Rovers
- NXP Training ContentNXP Training Content
- University ProgramsUniversity Programs
- Rapid IoT
- NXP Designs
- SafeAssure-Community
- OSS Security & Maintenance
- Using Our Community
-
-
- Home
- :
- Software Forums
- :
- S32 Design Studio Knowledge Base
- :
- HOWTO: Debugging SPT on S32R45 Using S32 Debugger
HOWTO: Debugging SPT on S32R45 Using S32 Debugger
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
HOWTO: Debugging SPT on S32R45 Using S32 Debugger
HOWTO: Debugging SPT on S32R45 Using S32 Debugger
The NXP device S32R45 has accelerators that can be programmed. The S32 Debugger included within the S32 Design Studio for S32 Platform IDE with the S32 Debug Probe provides the ability to debug these accelerators. The accelerator covered in this document: Signal Processing Toolbox (SPT).
Section map:
Preparation
Setup the software tools
Setup the hardware
Procedure
Create A New Debug Configuration
Start A Debug Session
Multi-Core
Preparation
- Setup the software tools
- Install S32 Design Studio for S32 Platform
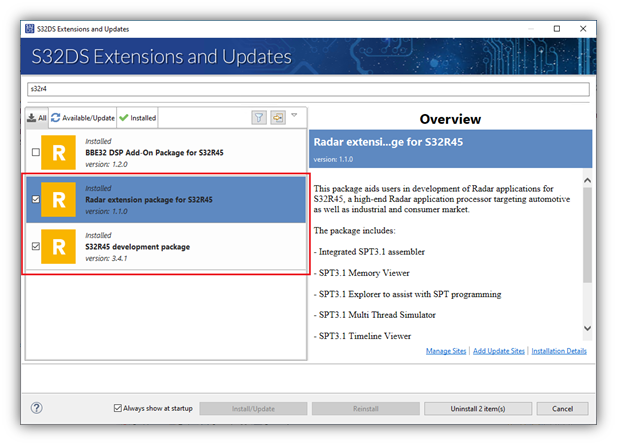
- Install the S32R4xx development package and the Radar extension package for s32R4xx. Both of these are required for the SPT accelerator.
- Setup the hardware
- Confirm the setup of the S32R45 evaluation board.
- Connect the power supply cable
- Setup the S32 Debug Probe. Refer to the S32 Debug Probe User Manual for installation instructions.
- Connect the S32 Debug Probe to the evaluation board via JTAG cable.
- Connect the S32 Debug Probe to the host PC via USB cable OR via Ethernet cable (via LAN or directly connected and configured for static IP address) and power supply connected to USB port.
- Confirm the setup of the S32R45 evaluation board.
- Launch S32 Design Studio for S32 Platform
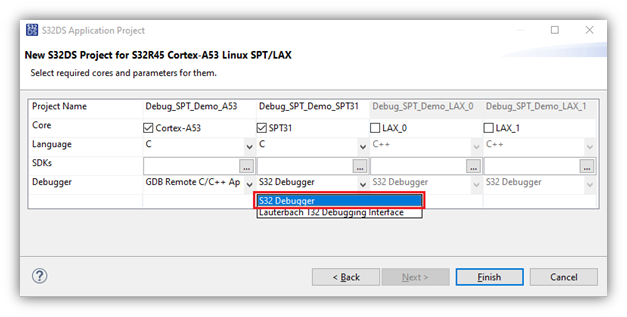
- Open existing project or create a new project and check that it successfully builds. If creating a new project, be sure the S32 Debugger is selected in the New Project Wizard.
Procedure
The procedure for starting a debug session and accessing the associated accelerator-specific registers is detailed here.
Debugging SPT is only conducted through the multi-core method. The SPT executable is included within A53 executable, the A53 application loads the SPT executable to the SPT core and both A53 and SPT core are available for debugging. The debug connection is made to the two cores through one of two methods:
- Baremetal/Bareboard: the debugger connects to both the A53 and SPT cores using the probe over JTAG.
- Linux BSP: the debugger connects to the A53 core, which is running Linux BSP, using a remote Linux connection over Ethernet and then connects to the SPT core using the debug probe over JTAG.
Before a debug session can be started a debug configuration must exist.
Create A New Debug Configuration
If the New Project Wizard was used to create the project using the S32DS Application Project option, then there was an opportunity to select the desired debugger from within the wizard. If the desired debugger option was selected at this time, then the needed configuration already exists and will only require adjustments to the hardware connection settings.
If the New Project Wizard was not used to create the project OR the currently desired debugger was not the one selected at the time of project creation, a new debug configuration must be created.
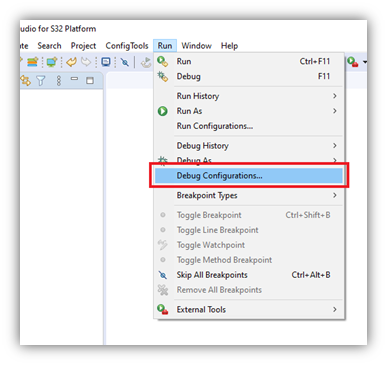
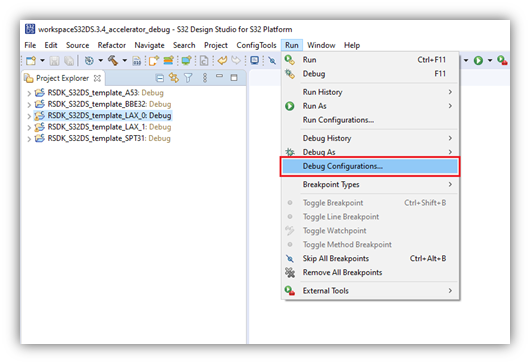
- With the existing project selected in Project Explorer, open the Debug Configurations Menu: Run -> Debug Configurations
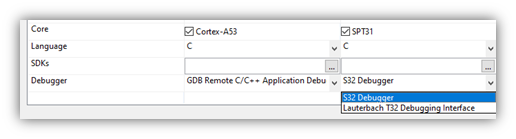
Having the existing project selected in the Project Explorer view will make the creation of a new launch configuration easier as many settings will be imported from the selected project. To select a project, click on it so it becomes highlighted. - Next, select the debugger for which the new debug configuration will be created.
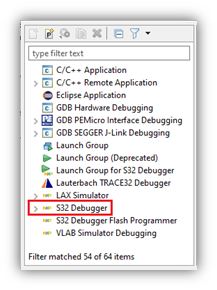
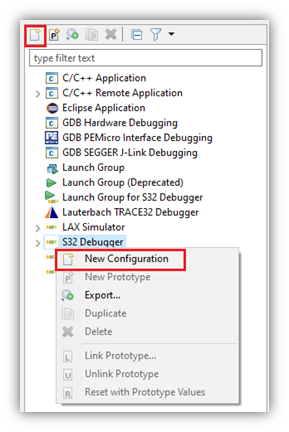
- To create the new configuration, either click on the ‘New launch configuration’ button from the toolbar at the top and to the left, or right-click on the ‘S32 Debugger’ and select ‘New Configuration’ from the menu.
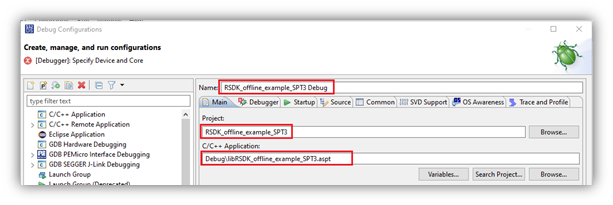
- Once the configuration is created it will be displayed and any errors with the configuration will be shown. If the project was selected in the Project Explorer, then the Name of the debug configuration will contain the project’s name and the Project and C/C++ Application fields will be populated as well. The C/C++ Application field will only be populated if the build output executable exists. Confirm these values are correct before moving on.
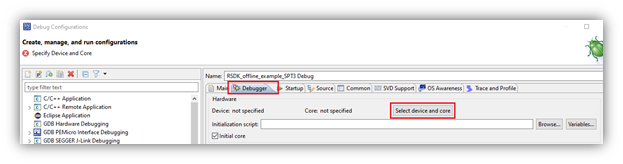
- There is an error showing that the Device core ID is not specified on the Debugger tab. Switch to the Debugger tab and click on the button ‘Select device and core’.
- From the Select Target Device and Core window, expand the listing until all cores are listed. Notice that all supported cores on the S32R45 are listed. Select the SPT31 core and click OK.
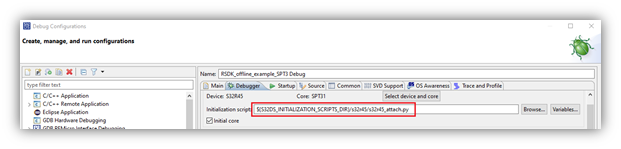
- Now that the device and core are selected, the attach script is selected automatically. The attach script will allow to start debugging on a core that is already initialized. This is correct for the SPT core as it is always launched in multicore scenario. Refer to the document 'README.txt' located in the same folder as these script files for details on all of the provided scripts.
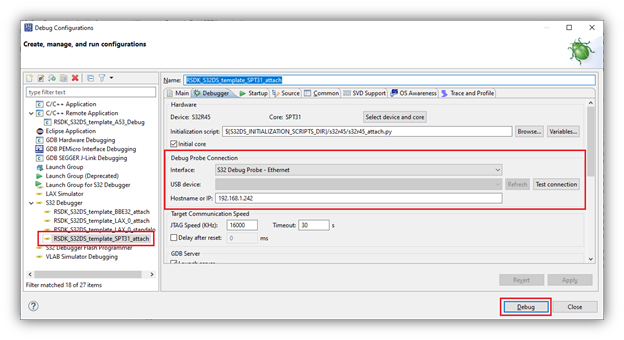
- Confirm the setting of the ‘Initial core’ checkbox. This box should be checked within the debug configuration that establishes the first connection to the target device via S32 Debug Probe. When this box is checked, the Debug Probe Connection interface and GDB Server settings become available. The probe connection only needs to be configured once and only one GDB Server needs to be running for each debug session. Therefore, this box should be checked for multicore debugging where A53 core is debugged via Remote Linux. If, however, the A53 and SPT cores are debugged via the S32 Debug Probe, then this box should be checked for the A53 debug configuration and should not be checked for the SPT debug configuration.
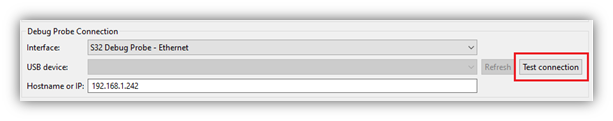
- If the ‘Initial core’ box was checked in the previous step, setup the Debug Probe Connection. Select either USB or Ethernet, depending upon your hardware setup. If USB is selected, the COM port for the S32 Debug Probe will automatically be detected (unless not connected or more than one probe is connected). If Ethernet is selected, then enter either the hostname (fsl + last 6 digits of MAC address) or IP address. It is highly recommended to press the ‘Test connection’ button to confirm the hardware connection is correctly configured. See the included ‘S32_Debug_Probe_User_Guide.pdf’ for more details on the setup of the S32 Debug Probe.
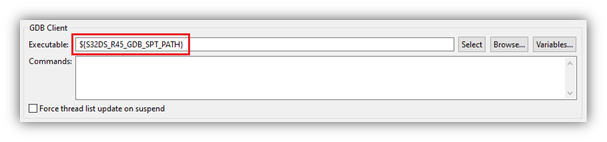
- Check that the GDB Client section has the correct path to the SPT GDB executable. It should point to the variable ‘S32DS_R45_GDB_SPT_PATH’.
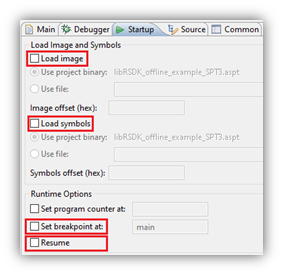
- Startup tab check the following settings
- Load image is NOT checked for multicore debugging. Basically, if it is loaded by A53 core (SPT executable is contained within A53 ELF file), then it does not need to be loaded.
- Load symbols is NOT checked. The SPT source file is assembly code, so there are no symbols to load.
- Set breakpoint at main and Resume are NOT checked for multicore debugging.
- After saving the new configuration with the ‘Apply’ button, SPT debugging can be performed.
Start A Debug Session
For convenience, the example project for S32 Design Studio from the RSDK, ‘RSDK_S32DS_template’, will be used to demonstrate multi-core A53/SPT debugging. The SPT core does not support standalone debugging. For instructions on loading this example project to your workspace, see ‘HOWTO: Create New Project from Example RSDK_S32DS_template from Radar SDK’.
A53 / SPT Multi-Core
For multi-core debugging, the A53 core is executing an application on the Linux BSP. The EVB should be setup to boot from a flash device which has been loaded with the S32R45 Linux BSP.
- Before beginning the debug sessions, be sure to load the driver dependencies (oal_driver, rsdk_spt_driver, and rsdk_lax_driver) as described in the RSDK User Manual, RSDK Offline Example section ‘Running the application’.
- Start A53 debug. From the menu at the top, select Run -> Debug Configurations…
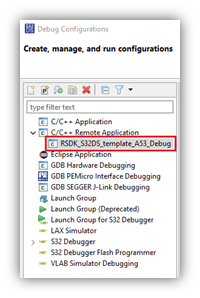
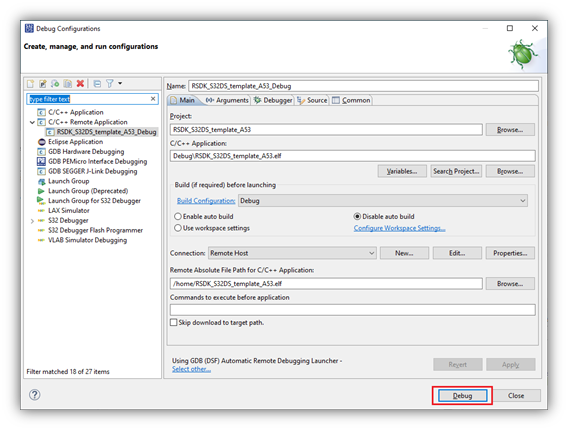
- In the Debug Configurations menu, from the configuration list, expand the ‘C/C++ Remote Application’ group and select the ‘RSDK_S32DS_template_A53_Debug’ configuration.
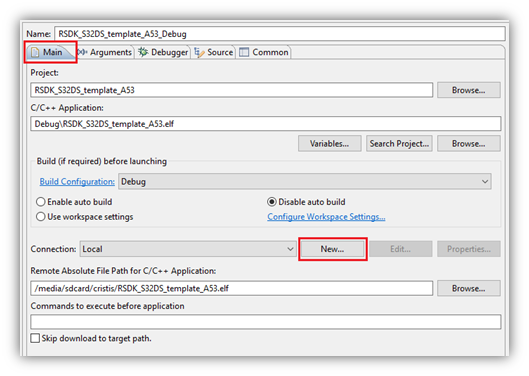
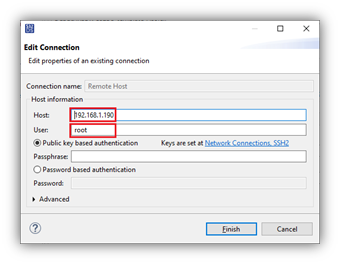
- On the Main tab, create a new connection for using the IP address of the EVB. The IP address could be determined either by issuing a Linux command over the serial connection, such as ‘ifconfig’, by accessing the local network connected device list, or perhaps the EVB was setup with a static IP address and it is already known.
- Click New… in the Connection section.
- Select ‘SSH’ for connection type.
- Enter the IP address in Host: field, use ‘root’ in User: field, and leave password field empty.
- Click New… in the Connection section.
- Click Debug to start debugging on the A53 core.
- The debugger will launch and execute until the first executable line in main(). See Debugger tab in Debug Configurations menu to adjust this setting.
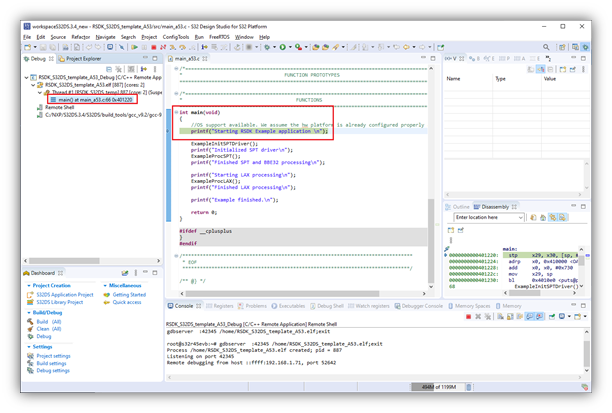
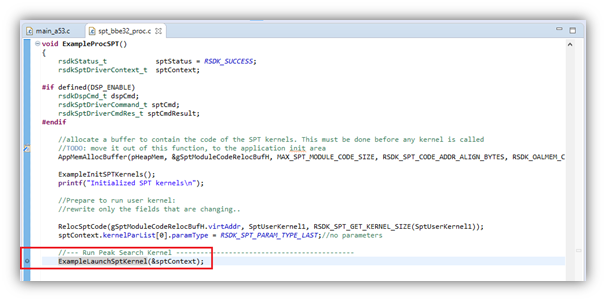
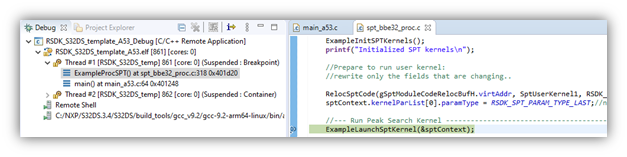
- Once the A53 debug session is running, advance the program counter to a line after the desired SPT kernel is loaded to memory but before the SPT kernel is launched. In the example here, this would be in ‘spt_bbe32_proc.c’, line 318, where ‘ExampleLaunchSptKernel()’ function is called. This is best done by setting a breakpoint on the line and clicking Resume.
- After the breakpoint is reached, the SPT debug session can be started.
- Return to the Debug Configurations menu, select the SPT debug configuration ‘RSDK_S32DS_template_SPT31_attach’, confirm the Debug Probe Connection settings and click Debug.
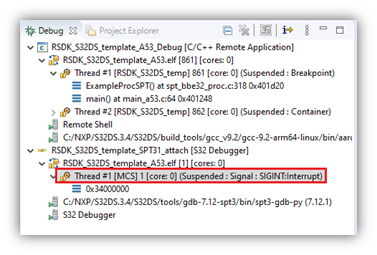
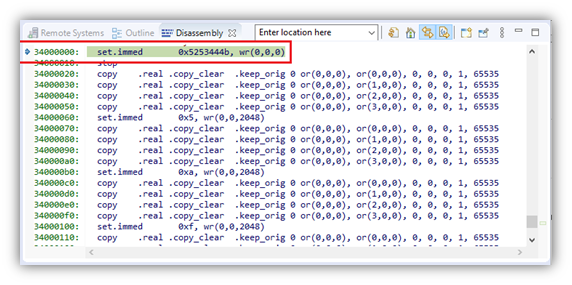
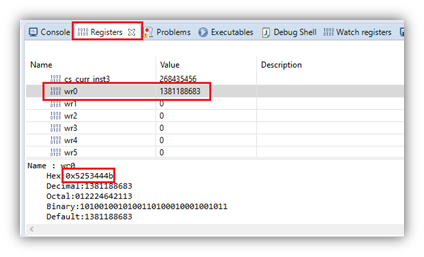
- Wait for the SPT debug session to launch and stop in the disassembly. Select the SPT debug thread to change the context of the Disassembly, Registers and etc.views. Now you can step through the assembly code, access registers, etc.